Research XRP: Disruptive Innovation or a Digital Mirage?

Analysis of the white paper
XRP is a cryptocurrency operating within the XRP Ledger (XRPL), an open-source, decentralized blockchain network created in 2012 by David Schwartz, Jed McCaleb, and Arthur Britto. XRPL facilitates fast and low-cost international transactions and supports various currencies and digital assets.
Main Technological Goals of XRP:
- Transaction Speed: XRPL enables the settlement of transactions within 3-5 seconds, offering a significant advantage over traditional payment systems.
- Low Transaction Costs: Transaction fees on XRPL are minimal, making it appealing to users seeking cost-effective payment solutions.
- Scalability: XRPL can handle up to 1,500 transactions per second, allowing for high user and transaction volumes simultaneously.
- Sustainability: XRPL is designed for minimal energy consumption, making it more environmentally friendly compared to other blockchains that rely on proof-of-work mechanisms.
Main Business Goals of XRP:
- Integration with Financial Systems: XRP aims to facilitate global financial transactions by acting as a bridge between different currencies and payment systems, enabling faster and cheaper international transfers.
- Adoption by Financial Institutions: Ripple, the company behind XRPL’s development, collaborates with banks and financial institutions worldwide, offering XRP-based solutions for cross-border transactions.
- Increasing Liquidity in Emerging Markets: With low costs and rapid transaction speeds, XRP can support the growth of markets with limited access to traditional financial services, enabling easier access to global finance.
In summary, XRP and XRP Ledger focus on delivering fast, low-cost, and sustainable payment solutions, with an emphasis on integration with existing financial systems and boosting global adoption among financial institutions.
Team and cooperation
The XRP project was created by Ripple Labs, founded in 2012 by Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb. Chris Larsen, co-founder and former CEO of Ripple, previously served as CEO of E-LOAN, one of the leading online lending platforms in the United States. Jed McCaleb, the other co-founder, is a well-known programmer who co-created BitTorrent and founded Mt. Gox, one of the first and largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world.
David Schwartz, Ripple’s Chief Technology Officer (CTO), plays a pivotal role in the Ripple Labs team. Schwartz is one of the primary architects of the XRP Ledger and has extensive experience in the field of distributed systems technology.
Ripple Labs collaborates with numerous financial institutions worldwide, including Bank of America, PNC Bank, Siam Commercial Bank, Santander Bank, and Standard Chartered Bank. These partnerships reflect the trust and credibility the Ripple team enjoys in the financial industry.
The Ripple Labs team consists of seasoned professionals with a wealth of experience in technology and finance. Their expertise, combined with strategic partnerships with renowned financial institutions, contributes to the success and credibility of the XRP project.
Evaluation of blockchain technology

The XRP Ledger (XRPL) is an open-source decentralized blockchain network designed for fast and efficient processing of financial transactions. Its architecture offers both high scalability and robust security mechanisms.
Scalability:
- Transaction throughput: XRPL can process up to 1,500 transactions per second, making it one of the fastest blockchains currently available. In comparison, Bitcoin processes approximately 7 and Ethereum around 15 transactions per second.
- Low latency: Transaction confirmation times on XRPL range between 3 to 5 seconds, enabling near-instant settlement, crucial for commercial and financial applications.
Security:
- Consensus mechanism: XRPL uses a unique consensus protocol where independent validators reach an agreement on transaction validity. This mechanism eliminates the need for energy-intensive proof-of-work processes while maintaining network integrity.
- Unique Node List (UNL): XRPL relies on a trusted list of nodes known as the Unique Node List (UNL), enhancing network security and consistency.
- Resilience to attacks: The XRPL network’s structure minimizes the risk of attacks, such as 51 percent attacks, due to its decentralized nature and consensus mechanisms.
Additional Features:
- Asset tokenization: XRPL enables the tokenization of various assets, including fiat currencies, precious metals, and other valuables, increasing its versatility for financial applications.
- Sustainability: Thanks to its efficient consensus mechanism, XRPL has low energy consumption, making it more environmentally friendly compared to traditional proof-of-work-based blockchains.
In summary, the XRP Ledger combines high scalability with robust security mechanisms, providing an efficient and sustainable solution for global financial transactions.
Tokenomics
XRP operating within the XRP Ledger (XRPL) has a blockchain designed to process global financial transactions quickly and efficiently. XRP Tokenomics covers the supply structure, distribution strategy and applications that highlight its key role in the ecosystem.
Token Structure and Distribution:
- Initial Supply: At the launch of XRPL in 2012, a total of 100 billion XRP tokens were pre-mined. Of this supply, 20% was allocated to the founders, while the remaining 80% was retained by Ripple Labs.
- Escrow Accounts: In 2017, Ripple Labs placed 55 billion XRP in escrow accounts to ensure predictable token supply. Each month, 1 billion XRP is released for operational use, with any unused tokens returned to escrow, controlling the rate of new token releases into circulation.
XRP Use Cases:
- Cross-Border Payments: XRP acts as a bridge currency, facilitating fast, low-cost international transactions. Its efficiency has made it an attractive solution for financial institutions seeking to streamline global payments.
- Asset Tokenization: XRPL enables the creation of tokens representing various assets, allowing them to be traded and transferred on XRPL’s built-in decentralized exchange.
- Medium of Exchange: XRP is increasingly accepted by businesses as a form of payment, enhancing its utility in everyday transactions.
Companies Accepting XRP as Payment
XRP is gaining traction as an acceptable form of payment across various industries. Below are examples of companies and platforms that accept XRP:
Platforms and Services Accepting XRP:
- Travala: A travel booking platform that allows payments in XRP for hotels and travel-related services.
- BitPay: A cryptocurrency payment service that integrates XRP, enabling businesses to accept this cryptocurrency.
- CoinGate: A cryptocurrency payment gateway supporting XRP, allowing merchants to accept payments in this currency.
- Crypto.com: A platform offering payment cards and financial services with the option to make payments in XRP.
Industries Accepting XRP:
- Media and Entertainment: Some platforms, such as Spotify, YouTube, Twitch, Imgur, Triller, and Cinnamon, accept XRP for their products and services or collaborate with Ripple to promote the cryptocurrency.
- E-commerce: Online stores offering electronics, clothing, or pet supplies are increasingly introducing XRP as a payment option.
- Travel and Tourism: Travel agencies, airlines, and hotels are enabling bookings paid with XRP, making international transactions more seamless.
Implementing XRP Payments:
Businesses interested in accepting XRP can use cryptocurrency payment gateways like Binance Pay, which provides integration with sales systems and supports multiple cryptocurrencies, including XRP.
Benefits of Accepting XRP:
- Fast Transactions: XRP enables near-instant payment processing, improving operational efficiency.
- Low Transaction Fees: Accepting XRP can lower the costs associated with payment processing compared to traditional methods.
- Global Reach: Cryptocurrencies allow businesses to access customers worldwide without currency barriers.
It is worth noting that the acceptance of XRP as a payment method depends on individual business decisions and may vary by region and industry specifics.
Deflationary Characteristics:
Every transaction on XRPL incurs a small fee, which is burned (destroyed), gradually reducing the total supply of XRP over time. While this process is slow, it contributes to the deflationary nature of the token.
In summary, XRP’s tokenomics are defined by a carefully managed distribution and supply control mechanisms that support its primary use cases, including cross-border payments, asset tokenization, and serving as a medium of exchange. Its deflationary properties add a unique dimension to its long-term supply dynamics.
Evaluation of competition

Ripple (XRP) operates in a highly competitive niche, focusing on cross-border payments, asset tokenization, and global financial inclusion. In recent years, numerous blockchain projects have emerged, offering alternative solutions and challenging XRP’s position in the international payments and financial institutions sector. Competitors such as Stellar (XLM) and Algorand (ALGO), as well as traditional financial entities like SWIFT, which are adapting their systems to compete with blockchain technologies, have created a dynamic and fast-evolving market.
Projects like Celo and Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) are also attempting to fill gaps in different market segments by providing unique approaches to payments, tokenization, and transaction management. Additionally, innovations in decentralized applications (dApps) and asset tokenization are drawing new players into the market, pushing Ripple to continually invest in its ecosystem to maintain its competitive edge.
Ripple faces competition on multiple fronts:
- From traditional financial systems, such as SWIFT, which dominate interbank financial transfers.
- From modern blockchains, which offer faster, cheaper, and more decentralized services.
- From regional projects, which aim to meet the specific needs of emerging markets or local economies.
While XRP distinguishes itself through strong partnerships with banks and financial institutions, its competitors are introducing innovations that demand Ripple stay ahead of the curve. This analysis examines XRP’s major competitors and their strategies, which could impact Ripple’s position in the blockchain ecosystem.
Regulatory Analysis of XRP

Ripple Labs, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency, is facing serious legal and regulatory challenges that have a significant impact on its business and the future of the XRP token.
SEC proceeding against Ripple
In December 2020, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) accused Ripple of conducting an unregistered securities offering by selling $1.3 billion worth of XRP tokens. The SEC argued that XRP should be treated as a security, which would require it to be registered. Ripple has vehemently denied these allegations, claiming that XRP is a digital currency, not a security.
Court ruling and SEC appeal
In July 2023, Judge Analisa Torres ruled that the sale of XRP on exchanges did not violate federal securities laws. However, institutional sales of XRP were found to violate these regulations. In October 2024, the SEC appealed the ruling, adding to the uncertainty over XRP’s regulatory future.
Impact on XRP’s price and reputation
Pending litigation has had a direct impact on the price of XRP, causing significant volatility. For example, after the SEC filed an appeal, the price of XRP fell by 11%. Lengthy legal battles have also affected Ripple’s reputation and investor confidence in XRP.
Changes in SEC leadership and their impact
In November 2024, it was announced that SEC Chairman Gary Gensler would step down in January 2025. His departure could affect the SEC’s approach to regulating cryptocurrencies, including XRP, potentially leading to a more favorable regulatory environment for digital assets.
Global regulatory challenges
Ripple faces a variety of regulations around the world, which complicates its business. Different approaches to cryptoassets in different jurisdictions require the company to constantly adapt to changing regulations, which generates additional costs and risks.
Ripple and XRP face serious legal and regulatory challenges that could affect their future. Ongoing litigation, particularly with the SEC, and changes in the agency’s leadership will be critical to XRP’s continued growth and adoption. The company must constantly monitor and adapt to the changing regulatory environment to ensure compliance and maintain the confidence of investors and business partners.
Security Audit: Verification of XRP Ledger Code and Features

Ripple (XRP) and its associated XRP Ledger (XRPL) focus on delivering a fast, scalable, and reliable blockchain for financial applications. Although XRPL does not support advanced smart contracts like Ethereum, security audits remain essential for its core codebase and additional features integrated into its ecosystem. Below is an analysis of the key areas:
XRP Ledger Code Audit
- Key Security Aspects:
The XRP Ledger source code is regularly audited to ensure security, particularly in areas critical to financial transactions:- Transaction validation mechanisms.
- Cryptographic algorithms for digital signatures and consensus.
- Protection against double-spending and Sybil attacks.
- Verification Processes:
Ripple Labs and the developer community conduct:- Static code analysis to detect vulnerabilities in the source code.
- Fuzz testing to simulate unexpected inputs and uncover weaknesses in the code.
- Recent Audit Results:
In recent years, no major vulnerabilities have been reported in the XRP Ledger, highlighting its robustness. However, continuous vigilance is required as new attack vectors emerge in the blockchain ecosystem.
Security of Escrow and Payment Channels
- Escrow Functionality:
XRPL provides an Escrow feature that allows funds to be locked and released under predefined conditions. This requires:- Strong cryptographic guarantees to prevent unauthorized fund releases.
- Transparent audit trails to monitor and prevent potential misuse.
- Payment Channels:
Designed for real-time off-chain transactions, payment channels rely on:- Secure state updates using cryptographic signatures.
- Protection against double-spending attacks.
Tokenization and Security of New Features
- Tokenization:
XRP Ledger enables the creation of tokens representing various assets. To ensure security:- Token issuers must follow best practices in issuance logic.
- Proper wallet and private key management is essential to prevent unauthorized token creation or transfers.
- Risks Associated with Tokens:
XRPL’s built-in decentralized exchange (DEX) can be exploited through maliciously deployed tokens or manipulated market orders, potentially harming users.
Third-Party Applications and Smart Contract Risks
Although XRP Ledger does not natively support advanced smart contracts, third-party applications can interact with XRPL:
- Third-Party Application Risks:
DeFi applications, token management tools, or payment platforms can introduce vulnerabilities. Each such application should undergo:- Audits by reputable blockchain security firms.
- Penetration testing to identify weaknesses.
- Malicious Integrations:
Any integration interacting with XRPL must be carefully vetted to avoid introducing vulnerabilities to the core network.
Ongoing Monitoring and Incident Response
- Bug Bounty Programs:
Ripple Labs runs bug bounty initiatives to encourage security researchers to report vulnerabilities. This proactive approach strengthens the ecosystem. - Incident Response:
The XRP Ledger team maintains an active incident response strategy to quickly address security issues and minimize risks.
Best Practices for XRPL Security
- Regular Audits:
Continuous audits of the XRP Ledger codebase and additional features are essential to ensure resilience against emerging threats. - Community Oversight:
As an open-source project, XRP Ledger benefits from the engagement of the developer community, which identifies vulnerabilities and suggests improvements. - Collaboration with External Firms:
Independent reviews conducted by leading blockchain security firms enhance the ecosystem’s trustworthiness. - Education and Awareness:
Token creators and application developers should be trained on blockchain security best practices to minimize errors and misconfigurations.
The XRP Ledger is widely regarded as secure and efficient, but its ecosystem requires constant monitoring to address new risks. Regular code audits, robust cryptographic protections, and collaboration with security firms are crucial to maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the XRPL network.
Questioning the Financial Compliance

An analysis of Ripple Labs’ financial statements, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency, has not publicly revealed any documented cases of accounting manipulation. However, Ripple Labs has been involved in several significant regulatory and legal issues that may raise concerns regarding its financial practices.
Regulatory and Legal Issues:
- Fine Imposed by FinCEN:
In May 2015, Ripple Labs was fined $700,000 by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) for “willful violations of the Bank Secrecy Act by operating as a money services business without registering with FinCEN.”
The company agreed to take corrective actions to ensure future compliance, including conducting XRP transactions and “Ripple Trade” activity exclusively through registered financial service providers. - SEC Lawsuit:
In December 2020, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) accused Ripple Labs and two of its top executives of conducting an unregistered securities offering worth $1.3 billion through XRP sales.
In July 2023, a court ruled that XRP sold by Ripple Labs is not a security; however, institutional sales or its use as a fundraising tool may be classified as securities under specific circumstances.
While there is no publicly available evidence of accounting manipulation in Ripple Labs’ financial statements, past regulatory and legal issues highlight the importance of thorough financial analysis and compliance. Investors and stakeholders should remain vigilant and regularly review financial reports and the company’s regulatory adherence to ensure transparency and integrity in its operations.
Field investigations

Conducting interviews with former Ripple Labs employees and analyzing the company’s operations in practice provides valuable insights into its functioning and the challenges it has faced.
Interviews with Former Employees:
Former Ripple Labs employees often highlight the company’s innovative approach and its commitment to revolutionizing international payment systems. They describe a dynamic work environment that fostered rapid technological development. However, some noted challenges related to regulatory compliance and the need to adapt to changing laws in various jurisdictions.
Analysis of the Company’s Operations in Practice:
- Collaboration with Financial Institutions:
Ripple Labs has partnered with numerous banks and financial institutions worldwide, enabling the integration of XRP Ledger technology into existing payment systems. An example includes a partnership with Santander Bank, which uses Ripple’s solutions for international transfers. (ripple.com) - Regulatory Challenges:
The company has faced numerous legal challenges, including a lawsuit from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in 2020, accusing Ripple of selling unregistered securities in the form of XRP tokens. In July 2023, a court ruled that the sale of XRP on exchanges did not violate securities laws, marking a partial victory for Ripple. (ripple.com) - Technological Development:
Ripple Labs continues to improve its technology, focusing on enhancing scalability, security, and cost efficiency. In May 2023, the company launched a platform for central banks and financial institutions focused on central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), built on the XRP Ledger.
To conclude, Ripple Labs demonstrates a strong commitment to developing innovative payment solutions while addressing regulatory and operational challenges. Insights from former employees and practical analysis of the company’s actions reveal its determination to integrate with the global financial system and adapt to a dynamically changing regulatory environment.
Analysis of ownership structure

An analysis of Ripple Labs’ ownership structure and capital transactions related to XRP reveals significant insights into ownership concentration and potential controversies.
XRP Ownership Structure:
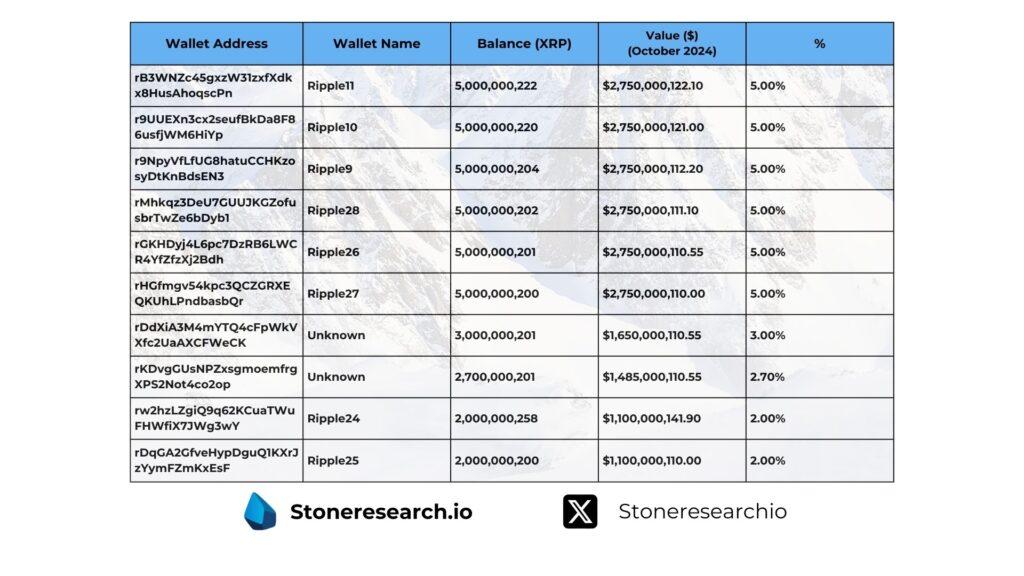
As of October 2024, the top 10 XRP holders control over 39% of the total token supply, while the top 100 wallets collectively own more than 72% of the supply. Among the largest holders are wallets attributed to Ripple, such as “Ripple11,” “Ripple10,” and “Ripple9,” each holding approximately 5 billion XRP, equivalent to 5% of the total supply.
Major investment firms:
- Andreessen Horowitz: In April 2013, this well-known venture capital firm invested $2.5 million in Ripple Labs, supporting the development of blockchain and cryptocurrency technology.
- Google Ventures (GV): In May 2013, GV, the investment arm of Google, invested $3 million in Ripple Labs during an angel funding round.
- IDG Capital Partners: In May 2015, IDG Capital Partners participated in a Series A funding round, investing in Ripple Labs.
- Santander InnoVentures: In October 2015, Spanish bank Santander’s venture capital fund invested $4 million in Ripple Labs.
- Standard Chartered: In September 2016, this international bank invested in Ripple Labs as part of a $55 million Series B funding round.
In 2024, Ripple Labs, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency, continues to work with a number of financial institutions and strategic partners. Although detailed information on new investors in XRP in 2024 is not publicly available, it is worth noting that XRP has gained in value, which may indicate growing interest from investors. Since the beginning of 2023, the price of XRP has risen by 10.7%, and forecasts for 2024 point to a further increase in the token’s value.
It’s also worth noting that in 2023 Ripple Labs acquired Swiss company Metaco for $250 million, expanding their offerings to include trust services for cryptocurrencies. In addition, Ripple has received preliminary approval for a payment license from the Central Bank of Singapore, allowing it to offer regulated payment token products and services in the region. Here’s a link to an article you might want to check out
Controversies and Suspected Capital Transactions:
Ripple Labs and its leadership have been involved in legal disputes regarding XRP sales. In December 2020, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) accused Ripple of selling unregistered securities in the form of XRP. In July 2023, a court ruled that XRP sales on exchanges did not violate securities laws, marking a partial victory for Ripple. However, Ripple was found liable for violating regulations in institutional sales and was fined a civil penalty of $125 million.
In October 2023, a court rejected the SEC’s appeal of the decision regarding Ripple Labs, which was considered a setback for the regulator.
The ownership structure of XRP shows a significant concentration among the largest holders, including Ripple Labs itself. The company has also been subject to regulatory investigations and legal disputes over the nature of XRP sales, resulting in substantial financial penalties. Nevertheless, Ripple continues to operate, partnering with financial institutions worldwide and advancing its payment technologies.
Forensic Report

Ripple Labs, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency, has been involved in several controversies and legal proceedings that raise concerns about its operations and business practices. Below are the key issues:
Market Manipulation Allegations
In the past, allegations arose that Ripple Labs controls a significant portion of XRP’s supply, raising concerns about potential price manipulation.
Although the company claims that XRP is a decentralized cryptocurrency, its large holdings of tokens lead to speculation about its ability to influence the market.
Reputational Challenges
In April 2024, Forbes described Ripple Labs as a “crypto zombie,” highlighting its struggles to disrupt traditional financial systems like SWIFT and noting that the company generated only $583,000 in fees in 2023. Additionally, Ripple holds $24 billion worth of XRP in escrow, which it can sell over the next four years, raising concerns about potential market impacts.
Partnerships and Financial Incentives
Ripple has established partnerships with various financial institutions to promote XRP’s adoption. However, reports suggest that Ripple provided financial incentives to partners, such as offering its software for free and subsidizing usage. For instance, MoneyGram received ongoing subsidies from Ripple, amounting to $8.9 million in the fourth quarter of 2019. Such practices have raised questions about the sustainability and genuine adoption of Ripple’s solutions
Partnership with MoneyGram
In 2019, Ripple invested $50 million in MoneyGram to enable the company to use Ripple’s technology for cross-border transactions. However, in 2021, MoneyGram suspended its partnership with Ripple due to the ongoing SEC litigation.
Questions About Technology
Ripple markets its solutions as blockchain-based. However, some experts, including Ripple’s CTO David Schwartz, have acknowledged that certain products, such as xCurrent, do not use blockchain or distributed ledger technology, which may mislead customers about the actual nature of these services.
Ripple Labs has faced multiple legal and regulatory challenges, including significant fines and allegations of misconduct. While the company has taken steps to address some issues, such as enhancing compliance programs, ongoing concerns about its business practices and leadership integrity persist. Investors and partners should exercise caution and conduct thorough due diligence when engaging with Ripple Labs and XRP.
Summary of Findings on Ripple Labs and XRP

Ripple Labs, the company behind the XRP Ledger and XRP cryptocurrency, demonstrates strong commitment to delivering innovative payment solutions characterized by speed, low costs, and scalability. However, an analysis of the project reveals both strengths and significant challenges:
Key Findings:
Technology and Functionality:
- The XRP Ledger (XRPL) features high scalability (up to 1,500 transactions per second) and fast settlement times (3-5 seconds).
- Planned innovations, such as Hooks (smart contracts) and federated sidechains, enhance XRPL’s versatility.
- Its eco-friendly approach (low carbon footprint) is an advantage over other blockchains reliant on proof-of-work.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Ripple Labs has faced significant legal disputes, including SEC allegations of selling XRP as unregistered securities.
- The company has taken corrective actions, such as implementing an AML program and collaborating with regulators to develop better legal frameworks for cryptocurrencies.
Ownership Structure:
- XRP shows a high concentration of ownership among a few major holders, including Ripple Labs, which may affect the perception of decentralization.
Investment Risks:
- Regulatory uncertainties surrounding XRP remain a significant risk.
- The project’s heavy reliance on Ripple Labs raises questions about its actual decentralization.
Investment Recommendations:
For Long-Term Investors:
- Positives: XRP offers strong technological fundamentals and global partnerships with financial institutions, making it an attractive choice in the realm of payment-focused cryptocurrencies.
- Risks: Investors should closely monitor regulatory developments, especially in the U.S., and track progress in the integration of smart contracts on XRPL.
For Short-Term Investors:
- XRP is sensitive to market volatility driven by regulatory events and partnership announcements. Short-term investments should incorporate active risk management.
General Recommendation:
- XRP can serve as portfolio diversification in cryptocurrency investments, but decisions should be made cautiously, considering legal risks and market concentration.
Ripple Labs and XRP present significant potential in the domain of international payments; however, investments in the project should be preceded by a thorough analysis of risks and long-term market strategy.
Price predictions for XRP in 2024 vary depending on analysts and sources. Below are some of the forecasts:
- CryptoNews: Predicts that by the end of 2024, XRP’s price could reach $1.51, assuming continued technological development and favorable regulatory outcomes. (cryptonews.com)
- CoinCodex: Based on data as of November 21, 2024, it predicts that XRP’s price in 2024 will range between $0.699874 and $1.15328. (forbes.com)
- Changelly: Estimates that in December 2024, XRP’s price will be between $0.928 and $1.54, with a potential return on investment of 207.9%. (changelly.com)
It is important to note that cryptocurrency price forecasts are highly uncertain and depend on various factors, including regulatory changes, market conditions, and technological developments. These predictions should be treated with caution, and regular monitoring of market updates is advisable.
Disclaimer: This is not financial or investment advice. You are responsible for any capital-related decisions you make, and only you are accountable for the results.
Source
https://xrpl.org/blog/2017/high-scalability-xrp-ledger
https://onxrp.com/tokenomics-of-xrp/
https://merchant.binance.com/pl/how-to-accept/xrp
https://coingate.com/blog/post/who-accepts-xrp
https://u.today/xrpl-smart-contract-hooks-passed-third-party-security-audit
https://ripple.com/insights/seven-leading-banks-join-ripples-global-network/
https://cointelegraph.com/news/sec-ripple-labs-liable-civil-penalty
https://decrypt.co/287069/sec-files-last-minute-appeal-in-ripple-case-why-xrp-army-outraged
https://cryptonews.com/price-predictions/xrp-price-prediction
