Research PetroChina: An Energy Giant at a Crossroads – Challenges, Opportunities, and the Future

PetroChina Company Limited is one of the world’s largest and most influential energy companies. It is a subsidiary of state-owned giant China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), which was established on April 5 1999, as part of a major restructuring of China’s energy sector. PetroChina plays a key role in achieving China’s energy goals, being the country’s largest producer of oil and natural gas and one of the leaders in the global energy commodities market.
The company operates in many fields, covering a comprehensive value chain in the oil and gas sector. Its activities include exploration and production of raw materials, oil refining, chemical production and the distribution and sale of energy products. In addition, PetroChina is developing its natural gas segment and investing in new energy sources, aligning itself with global trends related to the energy transition and decarbonization of the economy.
PetroChina was founded in response to the growing need for modernization and efficiency in China’s energy sector and to better utilize natural resources. Through listing on international stock exchanges such as the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange, the company has gained access to capital from global investors, enabling it to grow rapidly and increase its international prominence.
In recent years, PetroChina has faced many challenges. In the global market, it faces fluctuating oil and gas prices, increasing regulatory pressure related to environmental protection, and changing customer demands that are increasingly turning to more sustainable energy sources. The company is actively responding to these challenges by innovating, diversifying its operations and investing in renewable energy and energy storage technologies.
SWOT Analysis

Strengths (Internal Positive Factors)
Market Leadership
PetroChina is the largest producer of oil and natural gas in China, commanding a significant share of the domestic energy market. This leadership position makes it a cornerstone of the Chinese economy, which still relies heavily on traditional energy sources. A dominant position in the domestic market ensures stable revenue streams and influence, even amidst global market fluctuations.
State Backing
As a subsidiary of the state-owned China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), PetroChina enjoys substantial financial and strategic support from the Chinese government. This backing enables it to undertake high-risk projects, such as infrastructure development in remote areas or research into alternative energy sources, that might be infeasible for private firms.
Integrated Operations
PetroChina operates across the entire energy value chain, from exploration and production to refining, distribution, and retail. This vertical integration allows the company to control operational costs, minimize reliance on external suppliers, and diversify its revenue streams, ensuring long-term resilience.
Global Presence
Being listed on international stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, enhances PetroChina’s global visibility and provides access to international investors. This global presence strengthens its reputation and ability to secure funding for large-scale projects.
Technological Advancements
Continuous investment in research and development enables PetroChina to implement advanced technologies in exploration, production, and refining. Its recent focus on renewable energy technologies and energy efficiency positions the company for a leadership role in the evolving energy market.
Weaknesses (Internal Negative Factors)
Dependence on Fossil Fuels
A significant portion of PetroChina’s revenue is derived from oil and gas, making it highly susceptible to global shifts toward renewable energy. As the world moves toward greener energy, this dependency poses risks to the company’s long-term sustainability.
Environmental Criticism
The company has faced criticism for its environmental impact, including high greenhouse gas emissions and pollution. These actions attract scrutiny from environmental organizations and regulators, potentially increasing operational costs and harming the company’s reputation.
High Operating Costs
Exploration and production activities in challenging geographical regions, such as deserts or Arctic zones, are costly. Additionally, stricter environmental regulations worldwide necessitate significant investments to comply, further increasing expenses.
Geopolitical Risks
Close ties to the Chinese government may make PetroChina a target for international sanctions or trade restrictions, particularly in regions with strained political relations, such as the United States.
Slow Transition to Renewables
While PetroChina has invested in renewable energy, its pace of transition is slower compared to global competitors like Shell or BP. This delay may affect its competitiveness in the rapidly growing renewable energy market.
Opportunities (External Positive Factors)
Energy Transition
The global push for decarbonization and renewable energy presents a significant opportunity for PetroChina to diversify its portfolio. As part of China’s carbon neutrality strategy, PetroChina can play a critical role in the development of green technologies and clean energy.
Growing Energy Demand
Emerging economies, such as India and countries in sub-Saharan Africa, are increasing their energy consumption. PetroChina can leverage its resources and state support to expand its presence in these high-growth regions.
Strategic Partnerships
Collaborations with global energy firms and technology providers can accelerate PetroChina’s innovation and market entry in new energy sectors. Such partnerships could also facilitate the adoption of advanced technologies.
New Revenue Streams
Entering the metals trading sector, particularly in key materials like lithium and copper, positions PetroChina to capitalize on the global energy transition. These metals are essential for battery production and renewable energy infrastructure.
Government Initiatives
The Chinese government’s support for renewable energy and energy security initiatives aligns with PetroChina’s strategic goals. This backing can drive the implementation of large-scale projects and provide a competitive edge in the energy transition.
Threats (External Negative Factors)
Market Volatility
Fluctuating global prices for oil and natural gas significantly impact PetroChina’s revenues and profits. Overproduction or economic slowdowns can create an imbalance in supply and demand, leading to financial instability.
Regulatory Challenges
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations in China and internationally may force PetroChina to invest heavily in emission reduction technologies, raising operational costs and affecting profitability.
Intense Competition
Both domestic and international competitors, such as ExxonMobil, Shell, and BP, as well as emerging renewable energy companies, are aggressively vying for market share. This heightened competition threatens PetroChina’s dominance.
Geopolitical Tensions
Trade conflicts and political tensions between China and major economies, particularly the United States, could lead to restricted market access, sanctions, or limitations on technology sharing, negatively affecting the company’s operations.
Public Perception
Growing awareness of environmental sustainability among consumers and investors increases pressure on PetroChina to accelerate its energy transition. A perceived delay in adopting greener practices could harm its reputation and investor confidence.
PetroChina is a powerhouse in the global energy sector, leveraging its market dominance, state support, and integrated operations to maintain its leadership position. However, its reliance on fossil fuels and environmental challenges highlight significant internal vulnerabilities. The global energy transition, growing energy demand in emerging markets, and diversification opportunities offer pathways for growth. To thrive, PetroChina must embrace renewable energy adoption, mitigate regulatory and geopolitical risks, and enhance its sustainability efforts to align with global trends and stakeholder expectations.
Risk Analysis
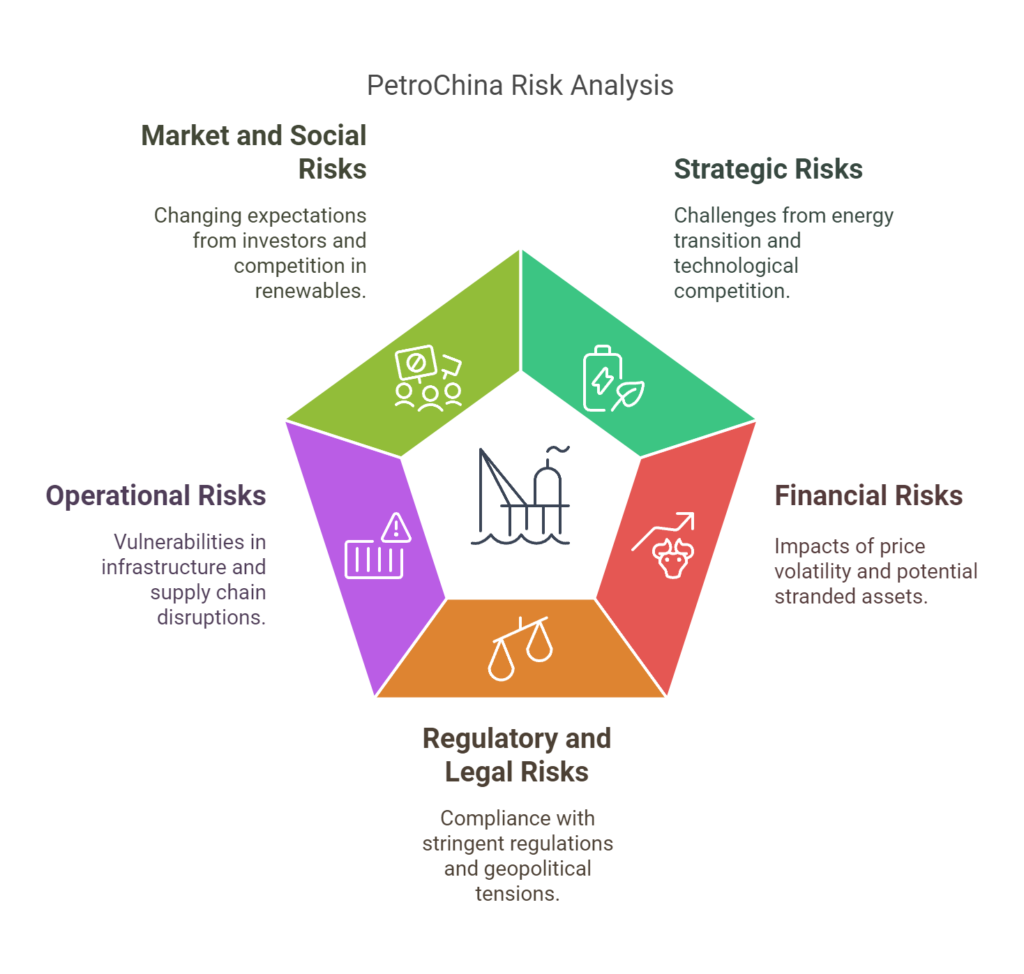
Strategic Risks
Energy Transition
PetroChina faces a significant challenge as the global energy market shifts toward renewable sources. Increasing pressure to reduce carbon emissions and align with climate commitments is reshaping the energy landscape, leaving traditional fossil fuel-based companies vulnerable.
- Threat: Declining global demand for oil and natural gas could significantly impact PetroChina’s revenue streams.
- Mitigation Actions: The company needs to accelerate investments in renewable energy projects, such as hydrogen, wind, and solar, while adopting aggressive decarbonization strategies to stay competitive in the evolving market.
Technological Competition
PetroChina competes with global giants like Shell, BP, and ExxonMobil, which are rapidly adopting innovative solutions in renewable energy and carbon reduction technologies.
- Threat: Delayed adoption of cutting-edge technologies may result in PetroChina falling behind its competitors.
- Mitigation Actions: Strengthen internal R&D capabilities and form strategic partnerships with technology-driven companies to gain access to the latest innovations.

Financial Risks
Price Volatility
The oil and gas markets are highly volatile, with prices influenced by geopolitical tensions, economic conditions, and global crises. Such fluctuations can severely affect PetroChina’s financial stability.
- Threat: Prolonged periods of low oil and gas prices could reduce profitability and limit the company’s ability to invest in new projects.
- Mitigation Actions: Develop additional revenue streams in renewable energy and key metal trading while implementing hedging strategies to protect against price swings.
Stranded Assets
Investing heavily in new oil and gas projects could result in stranded assets as demand for fossil fuels diminishes over time due to global decarbonization efforts.
- Threat: Assets could become unprofitable before generating expected returns.
- Mitigation Actions: Redirect capital toward sustainable energy projects, such as green hydrogen and offshore wind, and carefully evaluate the long-term viability of new fossil fuel ventures.
Source: Bloomberg Sponsored
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Globally tightening regulations on carbon emissions and pollution require PetroChina to adapt its operations to meet stricter environmental standards.
- Threat: Compliance with new regulations may increase operational costs and reduce profit margins.
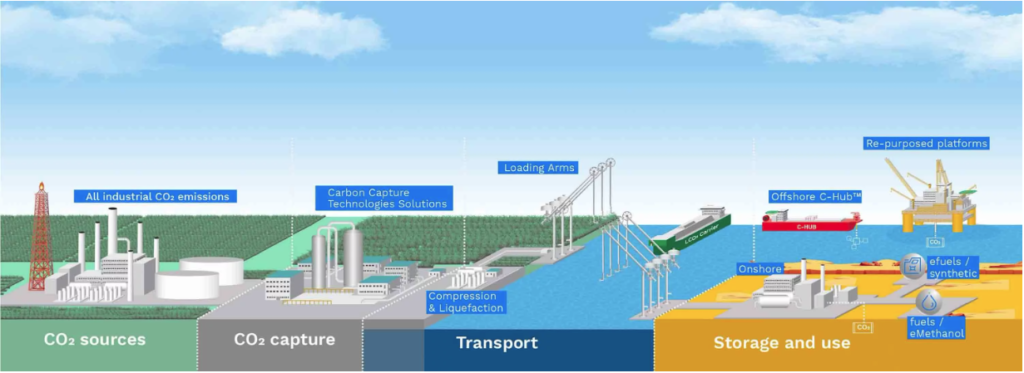
- Mitigation Actions: Invest in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies and enhance energy efficiency across operations to reduce emissions and align with regulatory expectations.
Geopolitical Tensions
As a state-owned enterprise, PetroChina is exposed to risks arising from geopolitical conflicts, particularly in regions with strained relations with China, such as the United States.
- Threat: Trade sanctions, restricted market access, or limitations on technology transfers could disrupt operations and growth.
- Mitigation Actions: Diversify geographic presence and strengthen local partnerships in key regions to minimize exposure to geopolitical risks.
Operational Risks
Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
PetroChina’s extensive network of pipelines, refineries, and exploration sites is exposed to risks from natural disasters, cyberattacks, and aging equipment.
- Threat: Disruptions in operations could lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
- Mitigation Actions: Modernize infrastructure, implement advanced monitoring systems, and invest in robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard critical assets.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains. Delays in securing critical components or equipment can impact project timelines and increase costs.
- Threat: Supply chain disruptions could hinder operational efficiency and project delivery.
- Mitigation Actions: Diversify suppliers and build strategic reserves to ensure continuity in operations during disruptions.
Market and Social Risks
Changing Investor and Consumer Expectations
Increasing awareness of environmental issues among investors and consumers is placing pressure on traditional oil and gas companies to improve their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
- Threat: Poor ESG performance could lead to declining stock values and reduced access to investment capital.
- Mitigation Actions: Enhance transparency in ESG reporting, implement sustainable practices, and actively communicate progress on environmental initiatives to stakeholders.
Competition in Renewable Energy
Existing and emerging players in the renewable energy sector are expanding rapidly, posing a threat to PetroChina’s market position.
- Threat: Delayed entry into the renewable energy market could result in a loss of market share in high-growth sectors.
- Mitigation Actions: Focus on scaling renewable energy projects and fostering innovation to remain competitive in the transition to green energy.
Environmental Risks
Climate Change
Extreme weather events, such as floods and hurricanes linked to climate change, pose operational risks to PetroChina’s infrastructure and supply chains.
- Threat: Natural disasters could disrupt operations, leading to financial and reputational damage.
- Mitigation Actions: Develop comprehensive disaster recovery plans and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.
Carbon Intensity
PetroChina’s carbon-intensive operations make it a target for criticism and regulatory penalties as the world moves toward stricter emission standards.
- Threat: High carbon emissions could harm PetroChina’s reputation and increase compliance costs.
- Mitigation Actions: Prioritize investments in CCUS technologies, improve operational sustainability, and set aggressive carbon reduction targets.
Summary of Risks
PetroChina operates in a challenging and dynamic environment, facing risks from energy transition pressures, regulatory changes, and market competition. Key threats include declining demand for fossil fuels, geopolitical tensions, and shifting consumer and investor expectations. To mitigate these risks, PetroChina must embrace renewable energy, diversify revenue streams, and strengthen its commitment to ESG principles. By proactively managing these challenges, the company can maintain its leadership position and thrive in the new era of sustainable energy.
Market Analysis

Global Energy Market Overview
Energy Transition
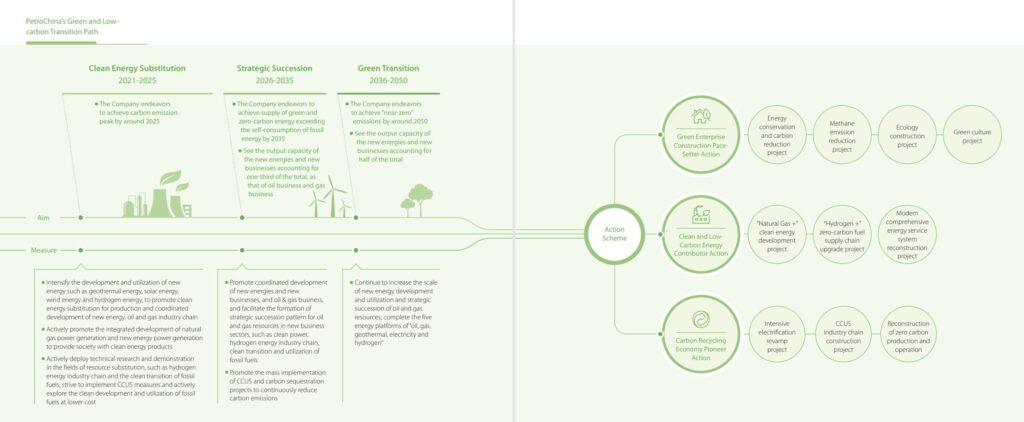
- The global energy market is undergoing a historic shift toward cleaner, more sustainable energy sources, driven by climate policies, technological advancements, and consumer demand for greener energy. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that renewable energy will account for over 50% of global electricity generation by 2050.
- PetroChina, as a traditional oil and gas company, is heavily exposed to the risks of declining demand for fossil fuels. However, this transition also presents opportunities to diversify into solar, wind, hydrogen, and carbon-neutral fuels.
Oil and Gas Market Dynamics
- Global oil prices have been increasingly volatile, influenced by factors such as geopolitical tensions, the OPEC+ production agreements, and economic uncertainties like recessions or slowdowns in major economies.
- Despite this volatility, natural gas remains a key growth area, particularly in Asia, where it is seen as a transitional energy source to replace coal. China’s growing LNG import needs further emphasize this trend. PetroChina, with its extensive infrastructure, can benefit from this demand but must also address the environmental pressures associated with gas production.
Regional Insights
- China: China remains one of the world’s largest energy consumers, driven by its industrial base and urbanization. However, the government’s commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 means PetroChina will face significant domestic pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and diversify its energy mix.
- Global Markets: PetroChina’s international investments in Central Asia, the Middle East, and Africa diversify its resource base but also expose it to geopolitical instability and competition from international oil majors.
Competitive Landscape
- PetroChina competes with major global players like ExxonMobil, Shell, BP, and Chevron, which are aggressively investing in renewables and advanced energy technologies. Domestically, PetroChina faces competition from Sinopec and CNOOC, particularly in refining and offshore exploration.
Key Trends
- Rising investment in hydrogen fuel, seen as a critical component of future energy systems.
- Increasing adoption of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies to meet emission targets.
- Growing demand for critical metals like lithium, nickel, and copper, which are essential for renewable energy infrastructure and electric vehicles. PetroChina’s entry into metals trading reflects recognition of this trend.
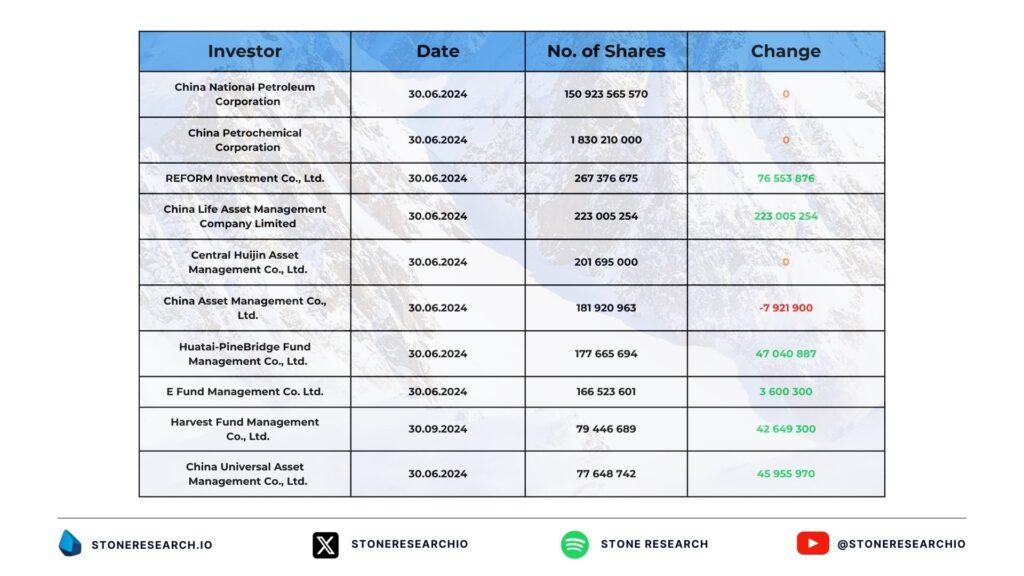
Major Shareholders
PetroChina Company Limited is one of the world’s oil and gas giants, playing a key role in the global energy market. As a subsidiary of China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), the company represents China’s technological and economic potential in the energy sector, while being one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases. Its presence on the Hong Kong and Shanghai stock exchanges attracts investors from different parts of the world, from sovereign wealth funds to individual investors.
State giant dominance: China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
- Shareholding: CNPC owns 80.25% of PetroChina, making it by far the largest shareholder.
- Strategic importance: CNPC is fully controlled by the Chinese government, and PetroChina is its main publicly listed subsidiary. CNPC manages PetroChina’s global operations, including the production, refining and export of oil and gas.
- CNPC’s global investments: The company operates in more than 30 countries with oil and gas projects in Africa, Asia and South America, increasing its importance in global energy policy.
Institutional investors
Although CNPC controls the majority of shares, the remaining 20% of PetroChina’s stock is publicly traded, attracting global financial players.
Major institutional investors:
BlackRock
- BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, has historically held a significant stake in PetroChina. Although its involvement is subject to volatile trends, the company remains on the list of important investors.
- BlackRock is under public pressure to invest in carbon-intensive companies, which could affect its future investment decisions.
Vanguard Group
- Vanguard is also one of the largest institutional investors in PetroChina. As the world’s second-largest asset manager, Vanguard influences the stability and perception of the company’s capital market.
- The company has been criticized in the past for its involvement in companies linked to human rights controversies.
Investment statistics
- Major trading markets: PetroChina shares are listed on the Hong Kong (H-shares) and Shanghai (A-shares) stock exchanges, allowing both international funds and local investors in China to invest.
- Investor breakdown: Among institutional investors, index funds dominate, investing in the company as part of larger portfolios of stocks included in stock market indexes.
Insider Investors in PetroChina
In the case of PetroChina, insider investors play a specific role that is closely tied to the dominant position of CNPC and its state-owned nature. Insiders are individuals with access to strategic decisions and key financial information of the company, and their actions can influence market perception and investor sentiment.
Role of Insiders in PetroChina
Board Members and Key Executives
- The board and directors of PetroChina are chosen from experts affiliated with CNPC and representatives of the Chinese government.
- Insiders are responsible for implementing China’s energy policy through PetroChina’s projects, both domestically and globally.
- Their decisions regarding company shares, such as selling or buying stock, are reported in compliance with stock exchange regulations in Hong Kong and Shanghai.
Representative Function
- Insiders act as ambassadors for CNPC in the global market. Through PetroChina, they promote the strategy of China’s energy sector, focusing on the development of international projects.
- Due to the centralized management structure, insiders in PetroChina have limited decision-making independence, as major financial and operational decisions are approved by CNPC.
Involvement in ESG Policies
- In recent years, PetroChina’s board, including insiders, has taken steps to integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives. Insiders must consider these factors in the company’s strategic plans to enhance its reputation in global financial markets.
Key Members of the Board
Chairperson of the Board
- This position is typically held by an individual from CNPC with extensive experience in the oil sector. The current chairperson is responsible for implementing CNPC’s long-term strategies through PetroChina.
Executive and Non-Executive Directors
- Executive directors handle the day-to-day operations of PetroChina, while non-executive directors represent the interests of CNPC and the Chinese government.
Independent Members
- Although PetroChina employs independent board members, their influence is limited since key decisions are shaped in Beijing.
Insiders’ Compensation and Shareholdings
- Insiders, including board members, often receive part of their compensation in the form of company shares, incentivizing them to achieve better financial results.
- Insiders’ shareholdings in PetroChina are publicly disclosed and monitored by the stock exchanges in Hong Kong and Shanghai.
Insider Trading Oversight
- PetroChina enforces strict regulations against insider trading to prevent the misuse of confidential information for personal gain. Insiders are required to report every transaction involving the company’s shares.
- Regulatory bodies such as the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX) regularly monitor insider activities, increasing the company’s transparency.
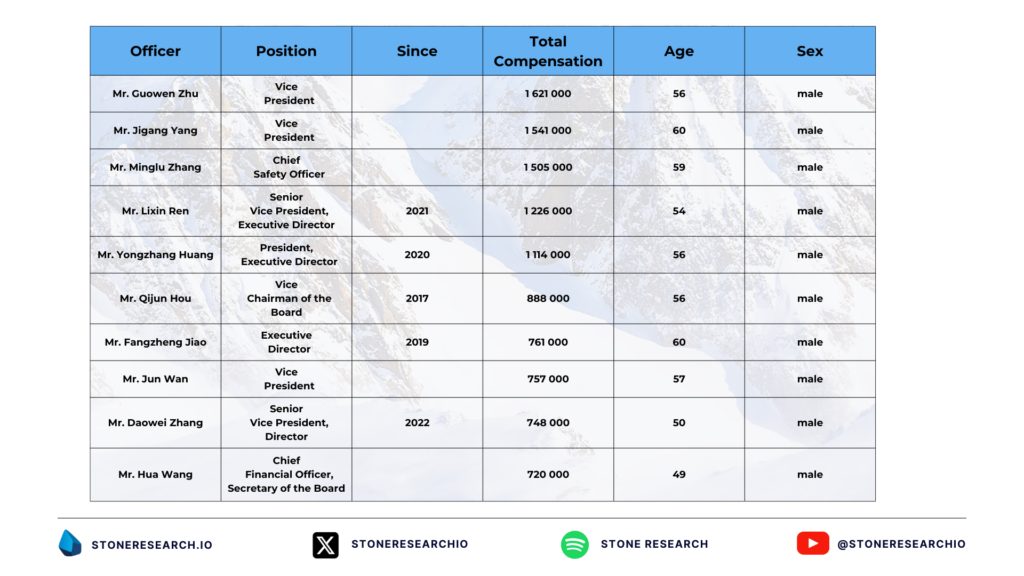
Forensic Report on PetroChina
PetroChina Company Limited, as one of China’s largest state-owned oil companies, has been involved in numerous legal violations, corruption cases, and trading irregularities in recent years. Below is a detailed forensic report on these incidents.
Corruption and Abuse of Power
Arrest of High-Ranking Officials (2013)
- In 2013, the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection announced investigations into four senior executives of CNPC and PetroChina for serious disciplinary violations.
- In June 2015, a former vice chairman was convicted of corruption-related crimes and sentenced to 15 years in prison.
Conviction of Former Vice Chairman (2017)
- In January 2017, Liao Yongyuan, former vice chairman of PetroChina, was sentenced to 15 years in prison for abuse of power and accepting $2 million in bribes.

Trading Irregularities
Illegal Oil Trading (2022)
- In January 2022, Chinese authorities fined PetroChina Fuel Oil Co Ltd for improper trading of imported crude oil, which severely disrupted the domestic petroleum market and caused tax revenue losses.
US Export Law Violations (2024)
- In June 2024, PetroChina International America Inc. agreed to pay a $14.5 million fine for violations of U.S. export laws.
- The company misclassified over $32 million worth of ultra-low sulfur diesel as a mineral oil blend while exporting it to Mexico between 2019 and 2020.

Environmental Violations
Explosion at Jilin Chemical Plant (2005)
- In November 2005, an explosion occurred at the PetroChina chemical plant in Jilin, resulting in 100 tons of benzene, a toxic and carcinogenic substance, entering the Songhua River. This cut off water supply to nearly 4 million residents of the city of Harbin for five days. The incident also affected the Russian city of Khabarovsk, where residents stockpiled bottled water. For a more extensive article click here
Lanzhou Water Pollution (2014)
- In 2014, PetroChina’s subsidiary, Lanzhou Petrochemical, was responsible for ethylene and ammonia leaks that contaminated drinking water in Lanzhou city. Municipal authorities criticized the company and demanded a public apology.
Response and Corrective Actions
Strengthening Internal Controls
- In response to these incidents, PetroChina has taken steps to enhance compliance mechanisms, including prevention, oversight, and accountability measures to avoid future violations.
Change of Auditor (2024)
- Following a financial scandal involving Evergrande, PetroChina terminated its auditing contract with PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) and revoked PwC’s nomination as its auditor for 2024.
PetroChina’s history has been marred by multiple corruption scandals, trading irregularities, and ethical violations. Despite implementing corrective actions, the company still faces challenges in rebuilding its reputation and ensuring compliance with international legal and ethical standards.
Speculative Information
Planned Closure of a Refinery in Northern China (2025)
According to sources cited by Reuters, PetroChina plans to shut down its largest domestic refinery in northern China around mid-2025. This would be the first significant closure of a state-owned refinery in China. The decision may be related to the restructuring of refinery operations and adaptation to changing market conditions.
Entry into Trading of Metals Essential for Energy Transition (2024)
In December 2024, PetroChina announced its plan to enter the trading of metals essential for the energy transition, such as copper and lithium. The newly formed team will be led by Richard Fu, a veteran of the commodities industry with over thirty years of experience. This strategic move aims to diversify the company’s operations and align with global trends toward renewable energy and electrification.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
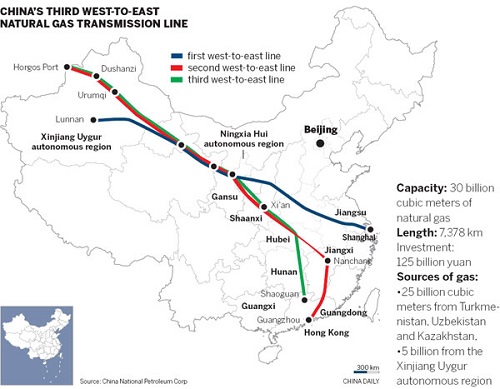
Controversies Surrounding the “West-to-East Gas” Project
PetroChina’s development of gas fields in the Tarim Basin in the Xinjiang region has sparked controversy due to potential environmental risks. Critics fear that the project could negatively impact local ecosystems and water resources. Nevertheless, the company continues its work, arguing that the project is crucial for national energy security.
Protests Against the Construction of a Petrochemical Plant in Chengdu (2008)
In 2008, PetroChina began constructing a $5.5 billion petrochemical plant in Chengdu. Despite assurances that significant funds would be allocated to environmental protection, residents feared potential pollution and organized peaceful protests against the investment. These demonstrations were one of the few instances of public opposition to industrial projects in China.

Summary
PetroChina Company Limited is one of the world’s largest oil and gas giants, playing a crucial role in China’s energy sector. As a subsidiary of the state-owned China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), the company dominates the Chinese oil and gas market. However, while PetroChina is a leader in fossil fuels, it faces significant challenges related to the global energy transition, environmental regulations, and commodity price volatility.
With strong government support, vertical integration, and international stock exchange listings, the company has solid foundations. However, pressures to decarbonize, geopolitical risks, and growing competition in the renewable energy sector could impact its long-term profitability.
Key Strengths of PetroChina
- Market Leadership in China – As the largest oil and gas producer in the country, PetroChina enjoys stable revenue streams.
- Government Support – The company is a key part of China’s energy policy and benefits from financial and regulatory backing.
- Diversified Operations – In addition to oil and gas exploration and refining, PetroChina is expanding into natural gas, chemicals, and commodity trading.
- Global Presence and Access to Capital – Listings on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX), New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), and Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) provide access to international investors.
- Investment in Innovation – The company is developing new technologies, including renewable energy, energy storage, and strategic metals trading.
Major Risks and Challenges
🔴 Dependency on Fossil Fuels – Despite investing in renewables, PetroChina still relies heavily on oil and gas, making it vulnerable to global decarbonization trends.
🔴 Regulatory Pressures – Both China and international organizations are tightening regulations on carbon emissions, requiring substantial investments in sustainability.
🔴 Geopolitical Risks – Sanctions, trade tensions, and restrictions on technology transfers could limit PetroChina’s international expansion.
🔴 Competition in Renewables – Global companies like Shell and BP are moving faster in the energy transition, which could weaken PetroChina’s position in the future.
🔴 Reputation and Environmental Issues – PetroChina has been involved in multiple scandals, including corruption, price manipulation, and environmental disasters.
Should You Invest in PetroChina?
Investment Advantages:
✅ Stable government support and a strong position in the Chinese market.
✅ Presence on global stock exchanges provides access to international capital.
✅ Opportunities for diversification in the renewable energy and strategic metals sectors.
Investment Risks:
⚠️ Heavy dependence on fossil fuels.
⚠️ High exposure to regulatory and environmental risks.
⚠️ Potential sanctions and trade restrictions.
For investors, PetroChina can be an attractive option, particularly for those seeking exposure to China’s energy market and willing to accept the high risks associated with geopolitics and the energy transition. The key success factor will be the pace of renewable energy adoption and the company’s ability to manage regulatory and financial risks.

Disclaimer: This is not financial or investment advice. You are responsible for any capital-related decisions you make, and only you are accountable for the results.
Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PetroChina
https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/energy-outlook.html
https://www.wsj.com/business/energy-oil/energy-utilities-roundup-market-talk-e9e5f633
https://www.ogdc.org/petrochina-signs-on-to-the-oil-gas-decarbonization-charter/
