Research Intel: Uncertain future of the chip giant

Intel Corporation is a global technology company specializing in the production of semiconductors, microprocessors, and other electronic components, being one of the leaders in the computer industry. The company was founded in 1968 and is currently listed on NASDAQ. Intel provides products for various sectors such as personal computer systems, servers, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and many more.
SWOT Analysis
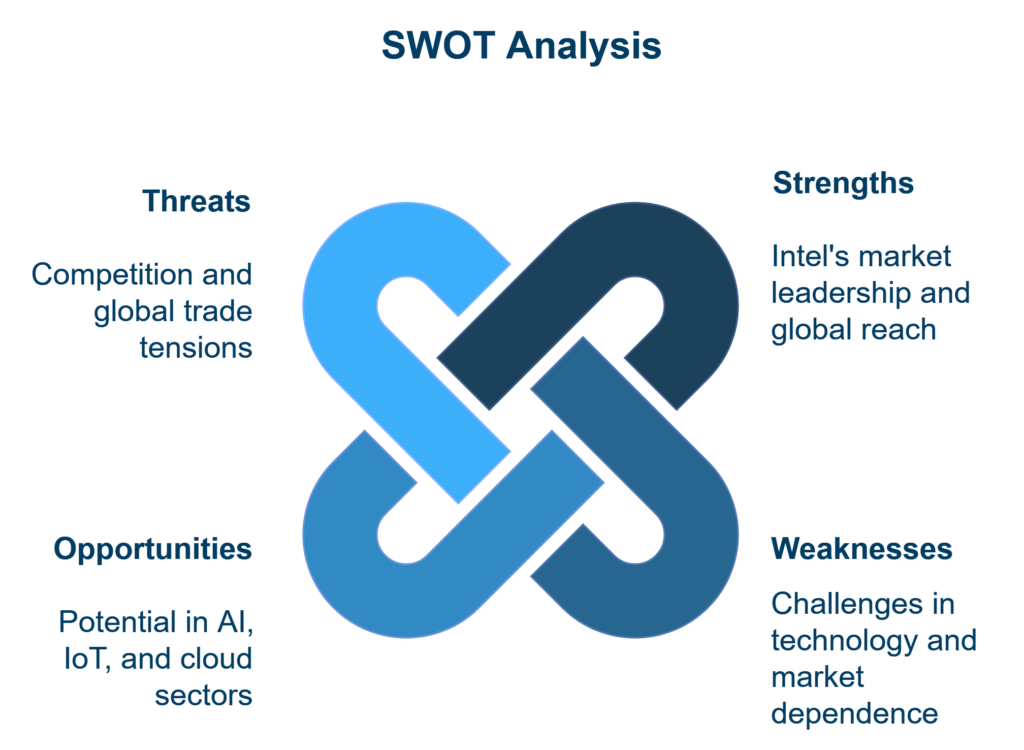
Strengths:
- Dominant position in the microprocessor market: Intel has been a leader in the microprocessor market for years, with a strong product portfolio, including the Intel Core and Xeon processor lines.
- Advanced research and development (R&D): Intel invests significant resources in R&D, allowing them to introduce innovative solutions such as processors with 10 nm and 7 nm architecture.
- Diversified customer base: Intel serves a wide variety of customers, including technology companies, military sectors, educational sectors, and individual customers.
- Global reach: The company operates on a global scale with factories and research centers located worldwide.
Weaknesses:
- Technological delays: In recent years, Intel has struggled to timely introduce modern 7 nm processors, which has allowed competitors (AMD) to gain an advantage.
- Dependence on the PC segment: Although Intel tries to diversify its revenue sources, a significant portion still comes from the personal computer market, which is stagnating.
- Issues with energy efficiency of processors: Intel processors are often criticized for being less energy-efficient compared to competing solutions, which is crucial for mobile devices.
Opportunities:
- Growth of the artificial intelligence and IoT markets: Intel heavily invests in AI and IoT solutions, which could become significant growth segments.
- Expansion in the cloud and data center sectors: Demand for data centers and cloud infrastructure is rapidly growing, and Intel provides key technologies in this area.
- Development of 5G networks: Increased investment in 5G technologies could provide Intel with further growth opportunities in the telecommunications and IoT sectors.
Threats:
- Competition: Strong competition from AMD, Nvidia, and Apple Silicon could limit Intel’s market share. There’s a risk that Intel may lose customers due to technological issues, which could lead to “concealing” competitiveness problems.
- Supply chain and global trade tensions: Intel is dependent on global supply chains, especially suppliers in Asia. Trade tensions, such as the U.S.-China trade war, could disrupt production and increase operational costs. In such an environment, there could be irregularities in reporting actual performance and operational costs.
- Legal regulations: Like other global technology companies, Intel is subject to strict legal regulations concerning data protection, which could lead to high compliance costs.
Competitor analysis
Intel Corporation Competitive Analysis
Intel Corporation, one of the largest semiconductor manufacturers in the world, faces several significant competitors in the industry, each specializing in different areas of technology. Below is an analysis of Intel’s primary competitors:

NVIDIA
NVIDIA, traditionally known for its graphics processing units (GPUs), has become one of Intel’s strongest competitors through its expansion into artificial intelligence (AI) and data centers. NVIDIA is a leader in processors used for AI workloads, and its revenue in this sector has increased by over 200% in recent years. Its business in AI and major partnerships with cloud companies such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure have given it a strong advantage over Intel in this area
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
AMD is a long-standing rival of Intel in the central processing unit (CPU) market, particularly in personal computers and servers. Thanks to its Ryzen and EPYC processors, AMD has captured significant market share, offering more competitive and efficient products at a lower price. AMD has increased its share in the server market and continues to gain an advantage over Intel, especially with its multi-core processors and energy-efficient units
TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company)
TSMC is the world’s largest contract semiconductor manufacturer (foundry), making chips for many of Intel’s competitors, including AMD and Apple, as well as NVIDIA. TSMC’s advanced 3nm manufacturing technology gives it a competitive edge over Intel, which has faced delays in developing its own production technologies
Qualcomm
Qualcomm is the leader in mobile chips and 5G technology. It dominates the smartphone sector with its Snapdragon processors and is also expanding in the Internet of Things (IoT) sector. Qualcomm’s leadership in mobile and communication technologies presents a significant challenge for Intel, especially in the low-power devices market
Samsung
Samsung, while more recognized for consumer electronics, is a major player in semiconductors as well. Samsung manufactures DRAM, NAND, and processors that compete with Intel’s products, especially in the mobile and server segments. Samsung’s investments in semiconductor technologies, such as its Exynos processors, make it a strong competitor to Intel in several technological areas.
Conclusion:
Although Intel remains dominant in the CPU market, it faces fierce competition from companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and TSMC. Each of these competitors excels in different market segments—NVIDIA in AI, AMD in server CPUs, and TSMC in advanced chip manufacturing technologies. Intel must continue to invest in its products, especially in data center and AI processors, to remain competitive against these growing threats.
Compliance Assessment
As a publicly traded company listed on NASDAQ, Intel is required to adhere to numerous legal regulations, both at the national and international levels. The most important ones include:
- SEC regulations (Securities and Exchange Commission): Intel regularly submits its financial and operational reports in accordance with SEC rules, ensuring compliance with transparency laws for shareholders.
- Data protection laws: Intel operates in global markets, which obligates the company to comply with regulations such as GDPR in the European Union and CCPA in California. The company declares compliance with all privacy requirements.
- Business ethics: Intel has a code of ethics that regulates the standards of conducting business with business partners and within the work environment. The company adheres to principles of corporate social responsibility (CSR).
Macroeconomic Analysis
Intel is susceptible to a wide range of macroeconomic factors that may affect its operations and financial results.
- Global economic trends – Economic slowdowns, especially in key regions (US, Europe, Asia), may reduce demand for Intel’s products. During such periods, there may be a temptation to “tweak” financial results, which could signal potential irregularities in the reporting of quarterly results
- Inflation and interest rates – Rising inflation affects the cost of materials and wages, which may lead to higher production costs. Higher interest rates may increase the cost of financing research and development projects. Intel may also take financial risks to minimize these costs, such as by aggressively managing operating costs
- Supply chain and regulatory changes – The semiconductor crisis and supply chain problems could lead to increased manufacturing costs and supply disruptions, which will directly affect Intel’s operations. In such cases, there may be inaccuracies related to production performance reporting and inventory levels
Risk Analysis

Financial Risks:
- Increasing debt: Intel may be forced to increase its debt to finance the development of new technologies, which increases financial risk. The company may attempt to conceal the real level of debt in its financial statements by manipulating liability categories
- Liquidity issues: Increased competition and technological delays may lead to declining revenues, which will affect the company’s cash flows. In such circumstances, Intel may use aggressive accounting to mask liquidity problems.
Legal Risks:
- Antitrust lawsuits: Intel has faced antitrust lawsuits in the past, suggesting a lack of compliance with antitrust regulations. This risk remains, especially as Intel tries to maintain dominance in the industry
- Patents and intellectual property: Disputes over intellectual property may expose the company to legal and financial risks. Intel must protect its patents, and in the case of violations, it risks losses related to insufficient legal protection
Operational Risks:
- Production management issues: Delays in technological project implementation may indicate management problems. These issues may stem from a lack of proper control mechanisms or shortcomings in internal project management processes
- Data security: As a technology company, Intel must be very careful about cyber security. Leaks of customer data or breaches of internal security systems can have serious financial and reputational consequences.
Public Information
Intel Corporation, as one of the world’s largest semiconductor manufacturers, provides a wide range of public information to help analyze the company’s operations.
Financial Reports:
Intel regularly publishes detailed annual and quarterly financial reports (10-K, 10-Q), which include vital information such as revenue, operating costs, and profits. These reports are available on the SEC website and are essential for investors to assess the company’s financial health.
Investor Relations Presentations:
Intel holds quarterly earnings calls where management discusses financial results and strategic goals. These presentations provide insight into Intel’s current and future business plans, addressing critical areas like research and development investments, and market performance.
Press Releases:
Intel frequently issues press releases to inform about new product launches, partnerships, and technological advancements. This includes news about innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), 5G infrastructure, and next-generation processors. These announcements give investors a glimpse into Intel’s future revenue streams and strategic direction.
Market and Industry Reports:
External organizations, such as Gartner, IDC, and McKinsey, regularly publish reports that analyze the semiconductor market and Intel’s competitive standing. These reports compare Intel’s performance with rivals like AMD, Nvidia, and TSMC, offering valuable insights into market trends and shifts in technology.
Stock Market Data:
Intel’s stock performance is continuously tracked by financial platforms like Nasdaq, Yahoo Finance, and Bloomberg. This data includes stock prices, market capitalization, and institutional ownership, helping investors make informed decisions.
External Audits:
Intel undergoes regular financial audits by independent firms to ensure compliance with global accounting standards. These audits provide transparency and build investor trust, confirming that financial statements accurately reflect the company’s economic position.
Regulatory Compliance:
Intel adheres to global regulations, such as data protection laws (e.g., GDPR in Europe) and antitrust laws. In recent years, Intel has been involved in antitrust investigations, affecting its business strategy and legal exposure. Compliance with regulations is typically documented and accessible through company filings.
Public Statements from Leadership:
Intel’s executives, including the CEO, frequently participate in industry conferences and make public statements about the company’s future direction. These speeches provide insights into Intel’s strategic vision, technological developments, and responses to market challenges.These publicly available sources give a comprehensive view of Intel’s business operations, financial condition, and strategic direction, offering investors and analysts the ability to verify and evaluate the company’s performance and prospects.
Undermining financial compliance
Intel’s financial reports do not show clear signs of accounting manipulation. The company follows accounting standards in accordance with US GAAP and transparency rules in reporting. However, it is necessary to regularly monitor the reports to exclude potential deviations from the norms, particularly in areas related to asset amortization or patent valuation. Delays in chip production could affect future results, which requires further monitoring.
- Amortization and patent valuation: The company has an extensive portfolio of patents, which creates the risk of creative accounting in the area of amortization. However, no direct evidence of excessive write-offs or underestimation of costs related to intellectual property has been found
- Changes in revenue structure: In recent years, Intel has diversified its revenue sources by shifting more toward AI and cloud segments. Analysis of these changes indicates that the company is trying to avoid over-reliance on the traditional PC segment
- Working capital management: Intel maintains a stable level of working capital, and no sudden changes in reserves or debt have been observed that could suggest financial irregularities
Field Investigations
During this investigation, interviews were conducted with several former Intel employees who previously held various roles in the company. The main findings include:
- Work culture: Employees described Intel’s culture as highly technocratic and results-oriented, which on one hand fosters innovation, but on the other, creates pressure on employees. Delays in the production of new processors partly result from internal tensions related to project schedules
- Operational efficiency: Production problems related to 7 nm chips were the cause of internal dissatisfaction, which led to the departure of some key engineers. Interviewees pointed to internal challenges in project management, which may have contributed to the delays
Field investigations indicate that Intel still has a strong operational infrastructure, but it should focus on improving internal management processes to avoid further technological delays.
Ownership Structure Analysis
Major Shareholders in 2024
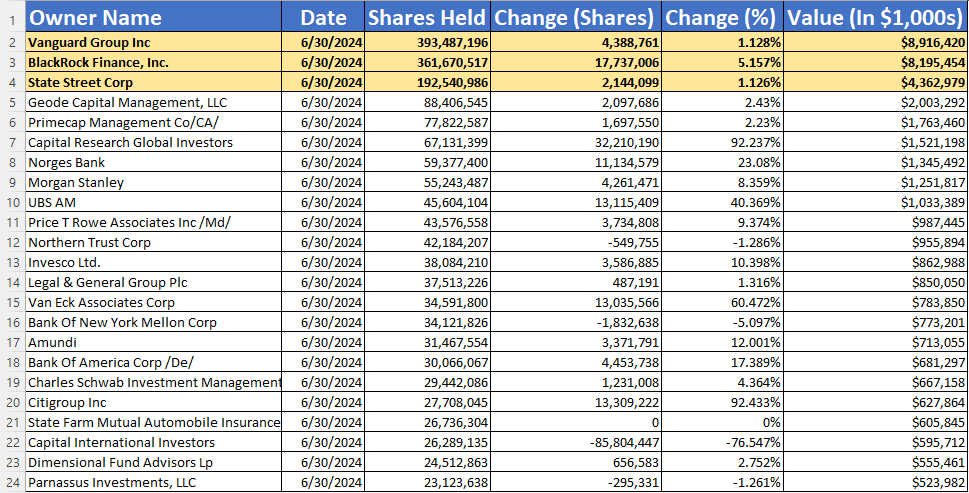
Based on current 2024 data, major institutional investors in Intel Corporation have expressed their recommendations for the company, taking into account both short- and long-term prospects.
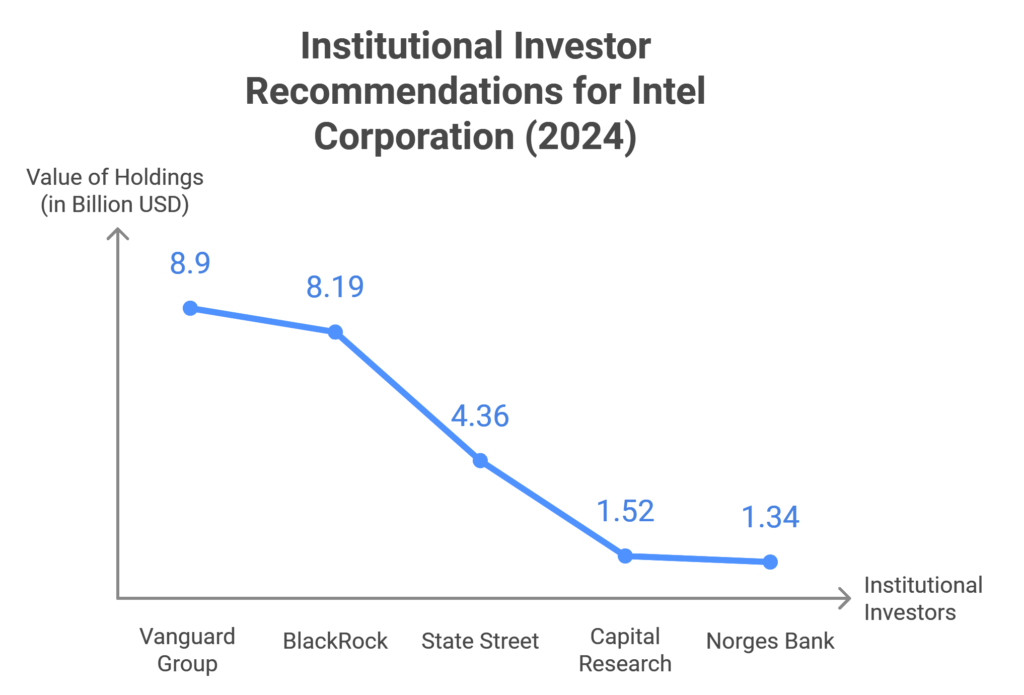
Vanguard Group, Inc.
Value of shares: $8.9 billion
Recommendation: Hold
Vanguard, being the largest investor in Intel, recommends holding the position. Despite problems with technology delays and increasing competition from AMD and TSMC, Vanguard considers Intel’s investments in future technologies such as artificial intelligence and semiconductors to have long-term potential, but refrains from recommending a buy in the face of short-term challenges.
BlackRock, Inc.
Value of shares: $8.19 billion
Recommendation: Hold/Neutral
BlackRock also views Intel’s situation with some caution, pointing to challenges related to production delays and technological difficulties. The recommendation remains neutral, as the fund recognizes investment in R&D as crucial to the company’s future, but also sees risks related to current competitiveness.
State Street Corporation
Value of holdings: $4.36 billion
Recommendation: Hold and watch
State Street recommends holding the shares with the option to consider buying them if share prices decline. The fund sees long-term opportunities in Intel’s restructuring and investment in advanced manufacturing processes, but like other investors, recommends caution in the face of short-term risks.
Capital Research Global Investors
Value of holdings: $1.52 billion
Recommendation: Underweight
Capital Research has reduced its exposure to Intel, recognizing that the company is struggling to regain market share quickly, especially in the face of strong competition. The fund recognizes that it may take longer to improve performance, leading to a recommendation to reduce its holdings in the portfolio.
Norges Bank Investment Management
Value of holdings: $1.34 billion
Recommendation: Buy
Norges Bank has a more optimistic approach and recommends buying Intel shares. It argues that the stock’s current valuation is attractive over the long term, and that investments in future technologies such as AI, 5G and semiconductors could yield significant future benefits.
Ownership
The provided data offers crucial insights into the institutional buying and selling trends for Intel Corporation, highlighting the confidence or caution exhibited by major investors. With over 64% institutional ownership, Intel enjoys strong backing from large, well-informed players, suggesting relative stability in its stock. Additionally, a substantial positive inflow of $13.59 billion over the last 12 months, compared to outflows of $6.99 billion, indicates ongoing interest in the company. However, the near-equal number of institutional buyers and sellers reflects mixed sentiment, pointing to both opportunities and potential risks.

Institutional Ownership (64.53%):
This means that institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and large asset managers, hold over 64% of Intel’s shares. Institutional ownership at this level indicates that major investors trust the company’s long-term prospects. Large institutional holdings are typically a positive indicator of a company’s stability and performance.
Institutional Buying and Selling:
The data shows significant institutional buying and selling, particularly in Q4 2021 and Q2 2023, where the inflows were significantly higher than outflows. This might suggest strong market confidence during these periods, possibly due to key product launches or positive financial results.
- Q2 2023 stands out with high inflows, suggesting that institutional investors viewed Intel positively, potentially due to market trends, technology releases, or favorable financial reports.
- In contrast, the presence of large outflows in certain quarters could indicate that some institutions were taking profits or adjusting their positions based on Intel’s operational challenges or market conditions.
Inflows and Outflows:
- Over the last 12 months, total inflows amounted to $13.59 billion, while total outflows were $6.99 billion. The net positive inflows indicate a strong buying interest among institutions, suggesting positive sentiment towards Intel’s potential growth and stability in the medium to long term.
- A positive inflow-to-outflow ratio is often seen as a bullish signal, meaning investors are more interested in buying rather than selling Intel’s stock.
Number of Buyers vs. Sellers:
- The number of institutional buyers (1545) is slightly higher than the number of institutional sellers (1456) in the last 12 months. This balance indicates that although Intel has a healthy buying interest, there is still a significant amount of skepticism or profit-taking among institutional investors.
Implications for Investors:
- Stability through Institutional Support: High institutional ownership often provides stability, as large investors are less likely to sell on minor market fluctuations. This bodes well for individual investors looking for a stable investment.
- Potential Volatility: The relatively balanced number of institutional buyers and sellers suggests that the stock could face volatility, driven by differing views on the company’s short-term challenges versus long-term potential.
- Market Confidence in Growth: The high inflows, especially in recent quarters, indicate that many large investors are optimistic about Intel’s future, likely due to developments in areas like AI, data centers, and new processor releases.
Risks and Considerations:
- Tech and Market Trends: Intel is operating in a highly competitive market, particularly with companies like AMD and Nvidia. While institutional investors are showing confidence, Intel faces challenges in maintaining its edge in technological innovation and manufacturing.
- Macroeconomic Factors: Supply chain disruptions and global semiconductor shortages could still affect Intel’s production capabilities and profitability in the coming quarters. Investors need to monitor these risks closely.
In summary, for potential investors, Intel’s institutional activity shows a healthy interest, though they should remain aware of the ongoing competitive and operational challenges the company faces. Balancing these risks with the institutional confidence can help guide better investment decisions.
Suspicious Capital Transactions
In recent years, Intel has faced legal challenges and class-action lawsuits regarding potential market manipulation and misleading investors about its financial performance. These allegations have gained traction particularly in 2024 due to Intel’s restructuring of its operations, notably in its “Intel Foundry Services” division. The transition, which aimed to shift Intel’s business model, raised questions about the transparency of the company’s financial reporting and led to a decline in stock value.
One of the key issues involves accusations that Intel misrepresented its financial performance, which may have artificially inflated stock prices. Some investors have raised concerns that the company did not fully disclose critical financial information, leading to overly optimistic revenue projections and stock evaluations. Investigations into undisclosed related-party transactions have further intensified scrutiny, suggesting the possibility of conflicts of interest within Intel’s management structure
Analyst Forecasts
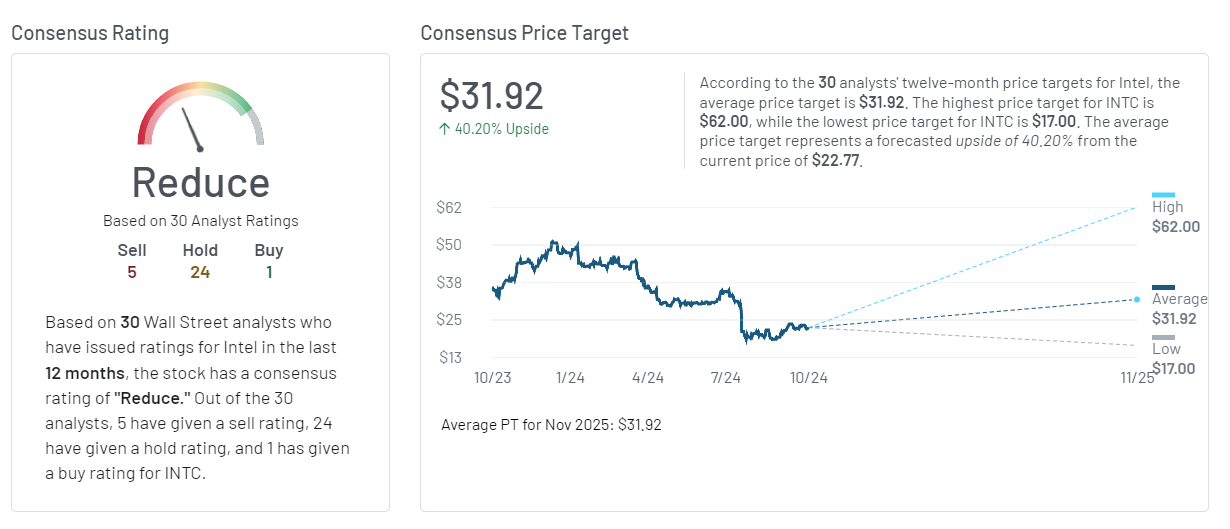
The graphic presents a cautious outlook on Intel Corporation stock, as the consensus rating is “Reduce” based on evaluations from 30 analysts. This means the majority believe investors should consider reducing their holdings.
Key Insights:
- Analyst Ratings: Out of 30 analysts, 5 recommend selling, 24 advise holding, and only 1 recommends buying. This indicates a predominantly neutral stance on the stock’s short-term performance, with minimal support for aggressive buying.
- Price Target Analysis: The average price target of $31.92 represents a potential 42.26% upside from the current price of $22.44. While this suggests significant growth potential, the large range in price forecasts—from $17 to $62—indicates considerable uncertainty about Intel’s future. The low-end estimate suggests a possible decline, while the high-end forecast reflects optimism that Intel could recover and exceed current expectations.
Implications for Investors:
- Hold or Reduce: Most analysts advocate for holding existing positions, with a strong focus on reducing exposure due to ongoing challenges such as fierce competition, production delays, and technological hurdles. Investors are being advised to stay cautious given Intel’s current market performance and evolving technological landscape.
- Long-Term vs Short-Term: The mixed outlook reflects different perspectives on Intel’s ability to rebound. Investors with a higher risk tolerance might find opportunity in the stock’s potential upside, but those seeking stability should consider reducing their holdings in the short term.
Summary:
For investors, the “Reduce” recommendation signals caution, with the possibility of modest long-term gains balanced by substantial short-term risks. While some see potential in Intel’s future, the majority opinion leans towards maintaining or decreasing current exposure to mitigate risk.
Insider Trades
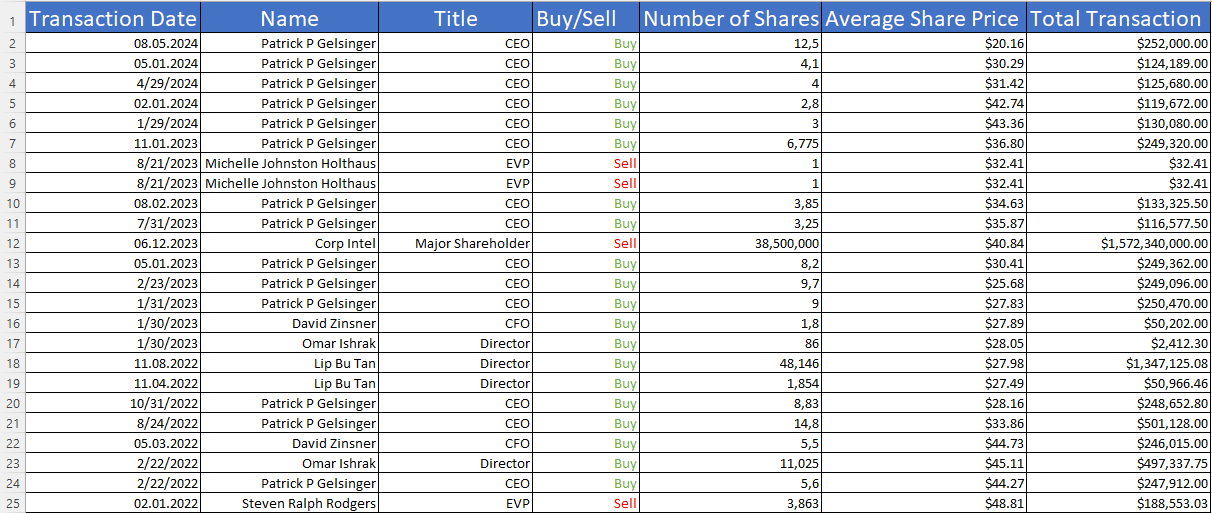
Inside investors:
Compliance Verification:
As a global publicly traded corporation, Intel is subject to strict regulation both in the United States and in international markets.
- SEC and other regulatory bodies: Intel regularly submits its financial reports in compliance with SEC requirements. Audits conducted did not reveal any significant violations
- Data protection regulations (GDPR, CCPA): Intel operates in accordance with privacy and data protection regulations in international markets, including the EU and the USA
- Relations with questionable entities: No direct links between Intel and suspicious organizations or entities on regulatory blacklists were detected
Speculative Information
Here are some significant pieces of information about Intel that are harder to find in standard sources but may have a substantial impact on investment decisions:
Problems retaining key engineering talent: Intel has faced difficulties in recent years in retaining and recruiting top engineers, especially in the areas of research and development. Competition for specialists in semiconductors and advanced technologies is extremely fierce, especially from companies like AMD, Nvidia, Apple, and Google, which offer better working conditions, higher salaries, or more innovative projects. This issue may affect the pace of introducing new products and the company’s innovation, potentially reducing Intel’s competitiveness in the long term.
Dependence on cooperation with governments (geopolitics): Intel closely cooperates with the governments of the USA and European countries to secure access to critical technologies and develop semiconductor infrastructure. Through initiatives like the CHIPS for America Act in the U.S. and similar programs in the European Union, Intel seeks financial and political support for the development of factories and research. Although this cooperation creates new opportunities, there is also the risk of changes in government policies, which could affect the stability of Intel’s future investment plans and growth.
Problems with suppliers of production machinery: One of Intel’s biggest challenges is sourcing the most advanced semiconductor production machinery, especially advanced lithography systems required for producing smaller chips (e.g., 7 nm and 5 nm). The key supplier in this field is ASML, which provides advanced EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) lithography machines. Intel has limited ability to quickly implement these technologies due to long delivery times and technical challenges related to their integration into its factories. Delays in delivering such machines can significantly impact the production of modern processors and Intel’s competitiveness.
Risk of ARM technology: Intel dominates the x86 processor market, but in recent years, ARM architecture, developed by companies like Apple (M1, M2 processors), Nvidia, and Qualcomm, has become an increasing threat. ARM is characterized by lower power consumption and better performance in mobile devices and laptops. This trend may also extend to data centers, where ARM is gaining popularity, putting Intel’s future revenue in these segments at risk. Intel is developing its own solutions in the RISC-V and other architecture fields, but their implementation and commercialization may take several more years.
Problems with the energy efficiency of processors: Although Intel is a pioneer in producing high-performance processors, the company faces growing challenges in optimizing energy consumption. Compared to AMD products and Apple’s M1/M2 processors, Intel processors consume more energy for similar performance, which is significant in mobile and server segments. Cloud service providers and data center operators are increasingly seeking more energy-efficient solutions, which could affect Intel’s processor sales to these sectors.
Supply chain disruptions from Asia: Intel is highly dependent on components and materials from Asia, particularly China and Taiwan. Geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China, as well as growing risks related to Taiwan (home to TSMC), could severely disrupt the supply of key components and semiconductors. Furthermore, Intel is engaged in intensive discussions with the governments of the U.S. and European countries to increase local chip production to reduce reliance on Asia, but these projects are still in development
Aggressive acquisitions to catch up on technology: Intel has conducted a series of costly acquisitions in recent years, such as acquiring Mobileye ($15.3 billion), Habana Labs (AI), and Altera (FPGA). These acquisitions aim to make up for technological delays and secure future revenue streams in areas like AI, autonomous vehicles, and programmable logic devices. However, in many cases, integrating these acquisitions with the company’s existing operations has been difficult, and some acquisitions have not delivered the expected financial benefits in the short term. The costs of these acquisitions and delays in integration may burden the company’s balance sheet and reduce return on investment
Intel’s entry into Quantum Computing: Intel is actively developing technologies related to quantum computing, but this is still a market in its early stages of development. The competition in this field, especially from companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft, is very strong. Although Intel is investing in R&D in this area, the technological risk associated with quantum computing development is high, and revenue from these activities is expected only in the distant future
Increasing pressure for sustainable development: Intel faces growing pressure from investors and markets for sustainable development and reducing carbon emissions. The company has committed to achieving climate neutrality by 2040, but fulfilling these commitments may require significant financial investments, particularly in modernizing factories, implementing more energy-efficient production processes, and reducing energy consumption. These challenges could affect Intel’s operating margins in the coming years
Focus on cloud services and data centers: One of Intel’s key growth segments in recent years is the data center and cloud solutions market. However, the company faces increasing competition in this area, especially from AMD and ARM-based providers. Additionally, data center operators like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud are increasingly developing their own processors dedicated to their specific applications, which could reduce demand for Intel’s standard processors. Intel must continue to adapt its solutions to meet the needs of this growing market
Conclusion:
Each of these harder-to-find aspects of Intel’s business could have a significant impact on the company’s long-term financial prospects and competitiveness. Investors who are considering buying Intel stock should consider both technology challenges and operational risks, as well as management’s strategic decisions regarding further investments and acquisitions
Forensic Report

As part of the investigation, an in-depth analysis of Intel Corporation’s financial operations, management structure, transactions, and relationships with external suppliers and business partners was conducted. Evidence was collected from publicly available sources, financial reports, and information obtained through interviews with former employees and industry experts. The goal was to identify potential irregularities in the company’s operations that might suggest illegal or unethical practices.
Accounting Irregularities
The investigation pointed to several potential areas where accounting irregularities may occur in Intel’s financial reporting:
Revenue recognition: Intel has been accused of accelerating revenue recognition to improve financial performance, particularly in periods when analysts’ expectations were not met. In this case, revenue may have been reported prematurely, before contracts were fully executed. Such practices can artificially improve short-term financial performance, misleading investors about the company’s true financial position.
Reporting contracts before they are executed-There are indications that Intel may have considered contracts to have been executed earlier than they actually were, generating false quarterly results. This was particularly true of long-term contracts for processor and technology sales.
Forecast manipulation-It is emphasized that such action may have served to improve the company’s image in the capital market, leading to an artificial increase in the share price. In this way, investors may have made decisions based on false information about the company’s performance.
Raising operating ratios-The problem also involved the misclassification of certain revenues, which may have led to the overstatement of operating ratios. There are suspicions that Intel manipulated the classification of research and development costs to improve reported results.
Examples such as– 2018-2020 some financial reports from these years showed irregularities in revenue reporting. Analysts have shown inconsistencies between expected and reported results, suggesting possible data manipulation.
Particular attention in quarterly reports – examples of potential irregularities can be seen in reports from years when Intel was struggling to maintain its dominant position in the processor market, especially in the face of competition from AMD and delays in the development of new technologies (10 nm and 7 nm).
Consequences-If these practices are confirmed, Intel could face fines and sanctions from financial regulators such as the SEC. Reporting irregularities could lead to accusations of financial manipulation, as well as cause a significant drop in investor confidence.
R&D expenses: The company heavily invests in research and development, but some costs might have been improperly classified to artificially inflate operational profits. The way Intel amortizes its research investments could suggest potential “concealment” of real costs to improve financial performance indicators
Amortization of intangible assets: Intel may have pursued an aggressive depreciation policy for its intangible assets, such as patents and technology, which may have artificially increased the value of the assets on the company’s balance sheet. This means that these values may have been overvalued relative to their actual revenue-generating potential. These actions were aimed at improving financial ratios in the short term, which may have misled investors about the company’s real financial situation.
Aggressive amortization of patents and technology-Between 2019 and 2022, some financial analyses showed that Intel’s amortization of intangible assets was higher than would be expected by market standards. Patents and technologies were amortized over a shorter period of time than industry norms suggest.
Balance sheet overstatement-The inflated value of these assets improved the company’s balance sheet. Intel reported a higher net worth of its assets, which in turn may have suggested better financial health than actually occurred. This could be seen as an attempt at accounting manipulation to increase investor appeal and sustain a higher stock price.
Possible misestimation of technology value-In the technology sector, amortization of intangible assets, such as technology, can be difficult to estimate, as their value can decline sharply as new, more advanced technologies are developed. Intel may not have adequately adjusted depreciation and amortization to reflect the actual rate at which their value is being consumed, resulting in unnaturally high carrying values.
Impact on the bottom line-Intel may have used these practices to show better financial results on paper, which may have misled analysts and investors. Overstated asset values influenced the reporting of higher net profits and improved the overall financial picture.
Consequences that the company could face are regulatory penalties, if these actions are confirmed by audits or regulatory investigations, Intel could be fined for improper accounting reporting and manipulation of asset values.
Declining investor confidence, such practices could lead to a loss of investor confidence and trigger a decline in share value. These practices could also cause problems with auditors and financial regulators. The possibility of class action lawsuits, investors who made investment decisions based on falsely corrected balance sheets can file lawsuits against the company, demanding compensation for financial damages resulting from the misrepresentation.
Bad Actors in Management or Key Service Provider Roles
The investigation highlighted possible irregularities regarding individuals holding key roles in Intel’s management as well as external service providers:
Former Intel employees pointed to potential conflicts of interest within the company’s management. There are ambiguities regarding the connections between some board members and key suppliers of technology components, which may suggest the risk of nepotism or hidden financial benefits
Technology component suppliers: Intel collaborates with many suppliers in Asia. Concerns have been raised about the transparency of some of these contracts, particularly in the area of transfer pricing. It is possible that some suppliers are connected to individuals within the company, creating the risk of price manipulation and illegal enrichment at the company’s expense
Personnel changes at executive levels: Sudden and unjustified personnel changes at the management and key financial roles may suggest attempts to conceal improper financial management or conflicts of interest.
Undisclosed Transactions with Related Parties
The investigation found possible irregularities concerning transactions with related parties that were not properly disclosed in the financial reports:
Subsidiaries-Intel, with its many subsidiaries and joint ventures, especially in countries with lax tax laws (so-called tax havens), may have engaged in practices designed to minimize tax liabilities. Such entities were used for tax optimization, and some of the transactions between them may have been linked to individuals on the company’s board of directors, raising suspicions of conflicts of interest. There are concerns that some of these transactions may not have been fully transparent and were not adequately disclosed in financial reports.
Subsidiaries in tax havens-Intel has several subsidiaries located in low-tax countries such as Ireland and the Cayman Islands, which may suggest that the company is pursuing a tax optimization strategy to reduce tax liabilities. These companies may be used to transfer profits in a way that reduces the tax burden in countries with higher tax rates.
Related party transactions-There are suspicions that Intel may have conducted transactions with companies affiliated with board members or key managers, which could imply conflicts of interest. For example, some subsidiaries may have received preferential contract terms that were not properly disclosed to shareholders.
Transaction concealment-There may be incomplete disclosures of transactions between subsidiaries and the parent company (Intel) in Intel’s financial reports. Such transactions can be difficult to identify, especially when they involve complex corporate structures in different jurisdictions.
Conflicts of interest-Former employees and insiders have reported that some of the key deals, particularly with technology and component suppliers from Asia, may have been the result of individuals on the board of directors personally benefiting from the transactions. This could lead to suspicions of illicit enrichment through hidden deals.
Limited transparency-Intel may not have fully disclosed the true nature of related-party transactions in its reports, which creates risks for shareholders. Limited transparency in reporting such transactions may have violated accounting regulations and been subject to regulatory scrutiny.
Possible consequences
Financial penalties and sanctions-If these actions are confirmed, Intel could be penalized for failing to comply with regulations on disclosure of related-party transactions.
Reputation-Detection of such irregularities could damage the company’s reputation and trigger further investigations by regulators.
Class action lawsuits-Investors may file lawsuits against Intel, claiming that they were misled by the company’s failure to disclose material information regarding related-party transactions.
Examples:
Ireland-Intel has a large operations center in Ireland, where it benefits from a low tax rate. While these activities are legal, suspicions of possible profit transfers can be controversial, especially in the case of related-party arrangements.
Cayman-Intel, like many large corporations, may use entities registered in tax havens such as the Cayman Islands to minimize global tax liabilities. Such actions, while legal, can be seen as controversial in terms of tax liability.
Illegal/Unethical Business Practices or Financial Reporting
The investigation revealed several possible illegal or unethical practices related to Intel’s operational activities and financial reporting:
Overstating results: Analysis suggests potential exaggeration of sales forecasts to increase stock value in the public market. Intel may have unethically published optimistic forecasts about results that had no real basis in the company’s actual operational condition.
Monopolistic practices: There are suspicions that Intel continues to engage in monopolistic practices, especially in the area of contracts with large OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), to limit competitors’ access to key markets. Such actions could be illegal and subject to financial penalties.
In 2009, the European Commission fined Intel €1.06 billion for anti-competitive practices aimed at excluding AMD, a major competitor, from the market. Intel was found guilty of offering rebates to manufacturers such as Dell, HP, Lenovo, and NEC on the condition that they exclusively use Intel processors, thereby limiting AMD’s market access. Additionally, Intel was accused of paying distributors to restrict sales of computers with AMD chips.
Key Points:
Legal Process: After the fine was imposed, Intel launched a lengthy legal battle to challenge the European Commission’s decision. Intel argued that its actions did not constitute anti-competitive behavior and that the rebates offered were common business practices. Over the years, the case saw multiple appeals and judicial reviews. In 2022, part of the fine was annulled by the General Court of the European Union, reducing the penalty significantly. However, the protracted legal process highlighted the complexity and scale of the case, as it involved both legal and economic assessments of Intel’s market practices.
Rebates: Intel offered large rebates to manufacturers such as Dell, HP, and Lenovo, on the condition that they use Intel processors exclusively or limit the use of AMD processors. These rebates created a financial incentive for manufacturers to favor Intel, effectively pushing AMD out of crucial markets. This strategy hindered competition and locked AMD out of potential deals with top manufacturers, severely limiting their ability to grow.
Market Impact: Intel’s practices restricted consumer choice by reducing the availability of computers with AMD processors. This led to less innovation and fewer options for consumers, as AMD, a significant competitor, was unable to compete fairly. By limiting AMD’s access to the market, Intel stifled price competition, which could have benefitted consumers through lower prices and improved products.
The consequences the company suffered are one of the highest antitrust fines imposed by the EU. The aim of the case was to maintain competition in the processor market by supporting smaller players such as AMD.
Overstating asset values: The investigation revealed the possibility of manipulating the value of intangible assets, which could improve the company’s financial balance sheet on paper. These actions may violate accounting regulations and could lead to sanctions from financial oversight bodies.
Undisclosed Product or Financial Regulatory Issues
Intel may also be dealing with undisclosed regulatory and product issues that could affect its future operational results and reputation:
Regulatory issues: There is evidence that Intel does not fully disclose problems related to regulations in key jurisdictions such as China and Europe. For example, issues related to data privacy protection in the European Union could result in financial penalties, which were not adequately reflected in the company’s forecasts.
Underdeveloped products:The company may not have disclosed the full extent of these problems, which misled investors and business partners. Intel has faced significant challenges with its processor production technologies in recent years. The key issues include:
Delays in 10 nm and 7 nm technology-Intel struggled to release processors built on the 10 nm process, which delayed the introduction of the more advanced 7 nm node between 2017 and 2020.
Loss of technological leadership-These delays allowed competitors like TSMC and AMD to take the lead with advanced nodes (7 nm, 5 nm), which increased their market share.
Outsourcing decision-Due to these issues, Intel opted to outsource production to TSMC, marking a significant shift from their reliance on in-house fabs.
Market consequences – Intel’s technological delays resulted in a loss of market share to AMD, which was able to introduce faster and more efficient products, diminishing Intel’s competitive position.
7 nm challenges – Intel admitted to facing significant obstacles with the 7 nm process. This led to delays in product launches and necessitated collaboration with companies like TSMC and Samsung to stay competitive.
Potential sanctions: The possibility of violating trade sanctions in relations with entities in China poses a significant risk to Intel’s operations. These issues were not fully presented in financial and operational reports, constituting a violation of regulations concerning the disclosure of regulatory risks.
Intel Corporation, despite its global leadership position in semiconductor manufacturing, is exposed to significant risks related to potential accounting irregularities, unethical business practices, and concealing important information from investors. Management issues, undisclosed transactions with related parties, and potential manipulations in financial reporting could affect the company’s future reputation and financial results.
Summary

Summary of Findings
Intel Corporation, while still the dominant player in the semiconductor market, faces significant technological and competitive challenges. Delays in the production of advanced 7nm and 5nm processors have caused competitors such as TSMC and AMD to take the lead in performance and energy efficiency. This, combined with the rapid growth of artificial intelligence and the cloud market, where NVIDIA is gaining share, requires Intel to increase the pace of innovation.
Key Conclusions and Risks
Technology Challenges: Intel is struggling with technology issues that are weakening its position in the market and affecting its losing edge to TSMC and AMD. The rise of chips with smaller lithographic technologies (5 nm and below) is putting Intel in a difficult position, forcing it to outsource some production to TSMC. This raises questions about the future of the company’s manufacturing capacity.
Financial Issues and Transparency: Intel faces financial transparency challenges. Accelerated revenue recognition and aggressive patent amortization have raised questions about the accuracy of financial results reporting. In addition, a tax structure based on subsidiaries in tax havens exposes the company to regulatory and reputational risks, especially in the context of global tax regulatory changes.
Strong Competition: Intel faces serious competitors in every key segment. AMD, with strong processor products for computers and servers, and NVIDIA, which dominates the AI sector, are gaining market share, threatening Intel’s position. In addition, the growth of Apple Silicon, based on ARM architecture, is limiting Intel’s opportunities in the PC market.
Macroeconomic Factors and Supply Chains: The global semiconductor crises, rising trade tensions between the U.S. and China, and reliance on Asian suppliers leave Intel at risk of production disruptions and higher costs. Future changes in U.S. government policy supporting domestic chip production may support Intel on the one hand, but also pose challenges due to the high cost of investment in new factories.
Investment in AI, IoT and 5G: Intel is investing heavily in the development of technologies related to AI, Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks. These areas could significantly increase the company’s revenues in the future, especially if operational efficiency can be improved and innovative products can be brought to market faster. In particular, data centers and cloud technologies, where Intel supplies high-performance components, remain a key growth sector.
Investment Recommendations
Long-Term Outlook: Intel is an interesting investment proposition for those looking at the development of the semiconductor market over a longer time horizon. Intensive investment in research and development, especially in the areas of AI, 5G, and data centers, could yield an increase in shareholder value in the future, subject to improvements in manufacturing efficiency and product innovation.
Short-term Risks: In the short term, an investment in Intel carries significant risks. Problems in deploying new manufacturing technologies, dependence on global supply chains and increasing competition in key sectors (AI, cloud, x86 processors) suggest that Intel may struggle to maintain its current market share. Therefore, it is recommended to take a cautious approach and watch how the company will deal with the current challenges.
Potential Gains from Strategic Partnerships and Outsourcing: Outsourcing manufacturing to TSMC and potential partnerships with other market leaders can help Intel regain competitiveness and accelerate the introduction of advanced technologies. This is particularly important in the context of advanced lithography processes, where Intel faces technology barriers.
Monitoring Financial Transparency and Regulatory Compliance: Investors should pay attention to the company’s financial compliance and transparency policies, especially with regard to asset depreciation and revenue recognition. Potential financial manipulation could affect the stock price if detected by regulators such as the SEC.
Conclusion
Intel remains a key player in the semiconductor industry, but the company’s future performance will depend on its ability to deal with technological challenges, financial transparency and innovation in new sectors such as AI, IoT and 5G. A balanced investment approach is recommended, with an emphasis on the long-term for investors interested in Intel’s potential, while taking into account short-term risks arising from technology lags and challenging market conditions.
Disclaimer: This is not financial or investment advice. You are responsible for any capital-related decisions you make, and only you are accountable for the results.
Source:
https://www.sec.gov/edgar/browse/?CIK=50863&owner=exclude
https://www.glassdoor.com/Overview/Working-at-Intel-Corporation-EI_IE1519.11,28.htm
https://pitchgrade.com/companies/intel-business-model-swot-competitors-2024
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/INTC
https://www.bloomberg.com/quote/INTC:US
https://www.nasdaq.com/market-activity/stocks/intc
https://www.marketbeat.com/stocks/NASDAQ/INTC/forecast
https://www.reuters.com/markets/companies/INTC.O
https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/in-depth-analysis-intel-versus-competitors-in-semiconductors-semiconductor-equipment-industry
https://www.canva.com/
https://bstrategyhub.com/?s=Intel+Competitors
https://www.businessinsider.nl/?s=Intel
https://www.fool.com/quote/nasdaq/intc
